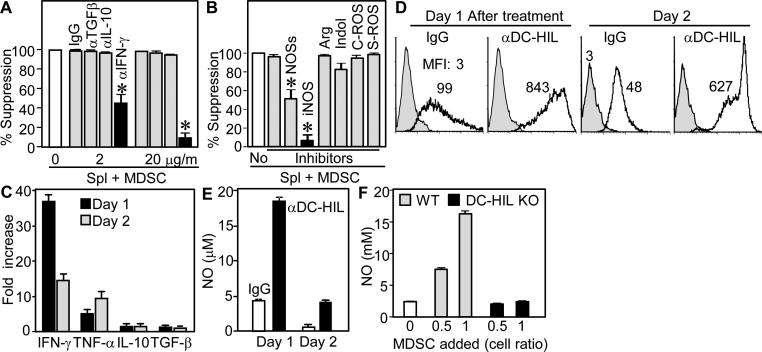
Figure 7. Activation of DC-HIL on MDSC induced expression of IFN-γ, NO, and ROS.
(A and B) Specific inhibitors were added separately to cocultures of spleen cells and MDSC (1:1 cell ratio) isolated from EAE-sick mice; including anti-cytokine Ab (A) and 5 mM L-NG-monomethyl-arginine citrate (inhibitor for NOSs); 0.5 mM N6-(1-iminoethyl)-L-lysine (iNOS); 1 mM N-hydroxyl-nor-arginine (Arg); 0.2 mM 1-methyl-tryptophan (Indol); 1,000 U/ml catalase (C-ROS); and 200 U/ml superoxide dismutase (S-ROS). Effects of inhibitors are expressed as % suppression relative to untreated coculture (set as 100%). (C through E) One or 2 days after culturing MDSC with immobilized anti-DC-HIL mAb or control IgG, cytokine secretion (C), ROS expression (D) and NO production (E) were measured by the cells. Cytokine expression is shown by fold increase relative to IgG-treated cultures. ROS expression is shown in gray-filled (untreated MDSC) or open (Ab-treated) histograms, with mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (F) Varying doses of MDSC from EAE-sick WT or DC-HIL−/− mice were added to spleen cell culture, and NO levels measured.