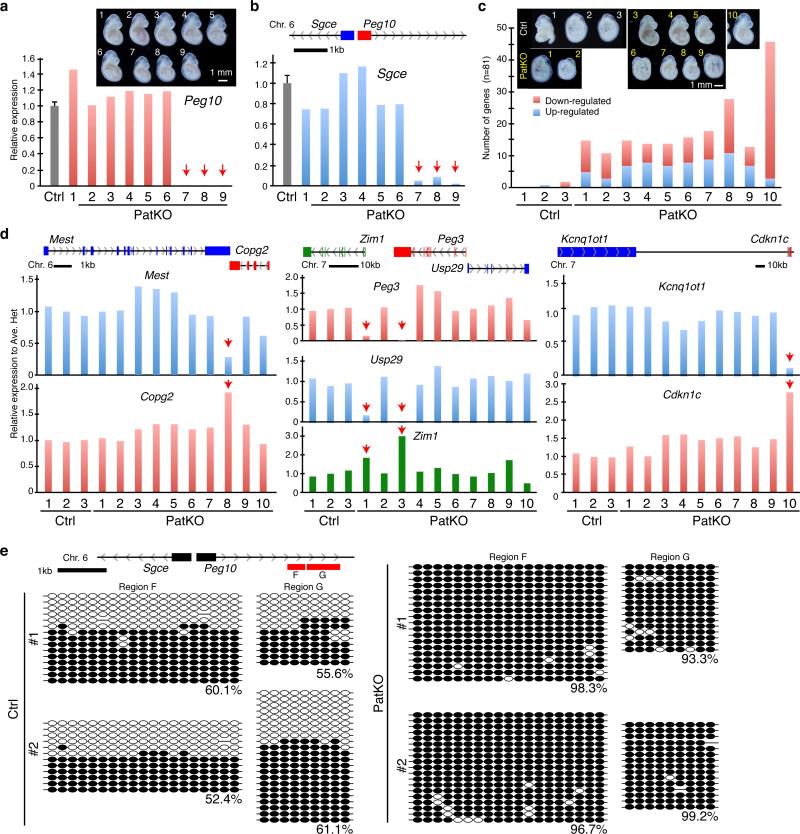
Figure 3. Tet1 paternal KO embryos and placentae exhibit imprinting defects.
a, b, RT-qPCR analysis of Peg10 (a) and Sgce (b) of E9.5 embryos from a single litter. The pup number corresponds to that in the inserted image in panel a. Arrows indicate the samples showing marked reduction in Peg10 and Sgce expression. The average value of Ctrl embryos (n=13) is set as 1. Error bar, S.E.M. Genomic location of Peg10 and Sgce genes is indicated at the top of the panel b. c, Number of up- and down-regulated imprinted genes in each of the PatKO embryos compared to the average FPKM (fragments per kilobase of exon per million fragments mapped) value of Ctrl embryos analyzed by RNA-seq (cutoff FC>1.5). A total of 81 autosomal imprinted genes expressed in embryos (FPKM > 0.4) are used in this analysis. The pup number corresponds to the inserted images. d, Relative expression level of imprinted genes at E9.5 embryos analyzed by RNA-seq. Arrows indicate the samples showing marked changes in expression levels. The average FPKM value of three Ctrl embryos is set as 1. The genomic locations of each gene are indicated at the top of the diagrams. The pup number corresponds to the inserted images in panel c. e, Bisulfite sequencing analysis of Peg10-DMR of E9.5 embryos. Analyzed region is indicated at the top of the diagram. Each CpG is represented by a circle with methylation and non-methylation represented by open and filled circles, respectively. The percentages of DNA methylation are indicated.