Figure 3.
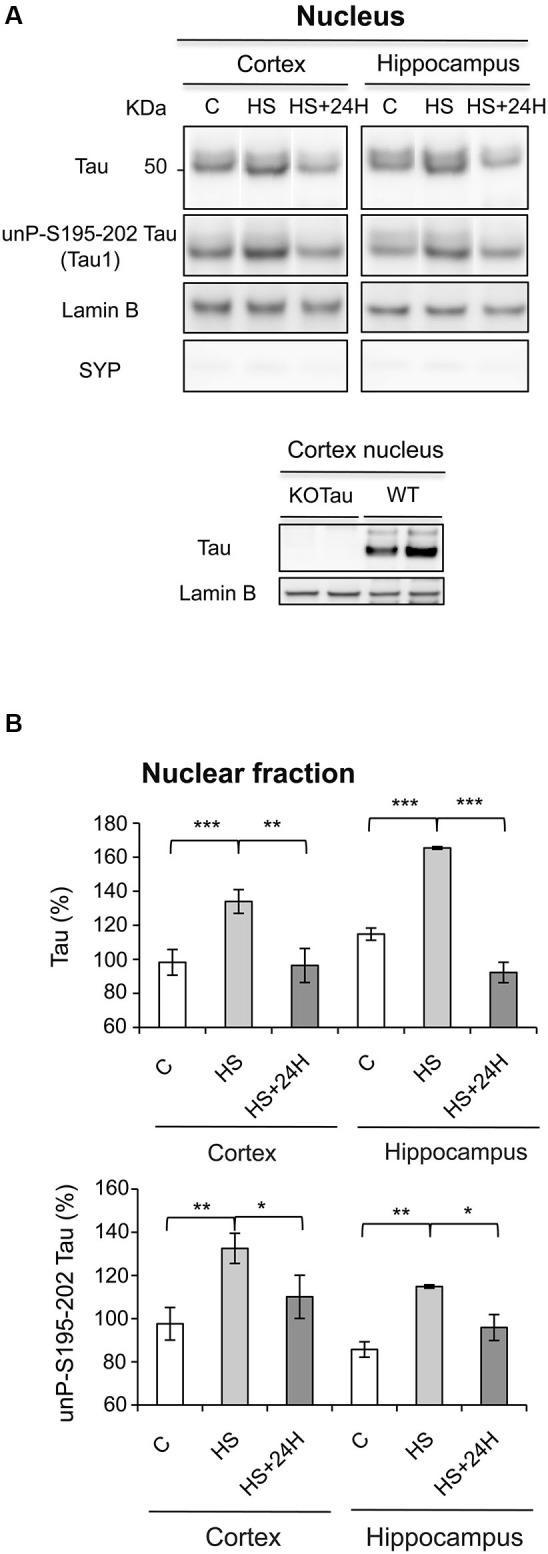
Nuclear Tau protects genomic DNA integrity from hyperthermia-induced damage. (A) Nuclear extracts from the cortex and hippocampus of WT mice in the control (C) condition, after HS or after a 24-h recovery after HS (HS+24 h) were analyzed using immunoblotting for Tau independent of phosphorylation (Tau) and Tau unphosphorylated at epitope S195-202 (Tau1). Lamin B and synaptophysin (SYP) were used as specific nuclear and cytoplasmic markers, respectively. (B) Densitometric analysis of Tau (normalized to lamin B) and Tau1 (normalized to total Tau) revealed an increase in Tau protein dephosphorylated at epitope S195-202 in the nuclei of neurons under HS. 24 h of recovery restored basal nuclear Tau levels. The data shown are the mean ± S.D. of three different mice. *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05.
