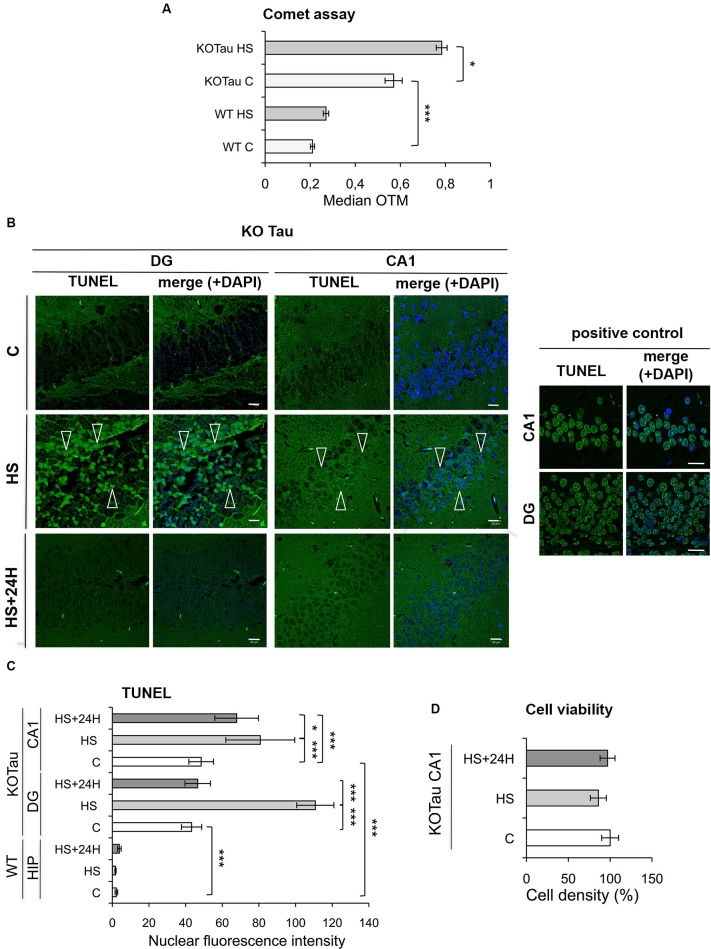
Figure 4.
Hyperthermia increases non-cytotoxic nucleic acid damage selectively in KO-Tau neurons. (A) The effect of Tau deficiency on genomic DNA integrity was measured using a Comet assay in control (C) and HS mice. The results are presented as the OTM from WT or KO-Tau cortices under C or HS conditions. Tau deficiency selectively promoted DNA damage accumulation and the majority of fragmentation under C and HS conditions. Each OTM value is the median value of 150–200 cells from three different cortices. *** p < 0.001; * p < 0.05. (B) Representative images of the dentate gyrus (DG) and CA1 sagittal sections from 7-month-old KO-Tau mice subjected to TUNEL assay under C, HS and 24 h recovery after HS (HS+24 h) conditions and analyzed using laser scanning confocal microscopy. Nuclei were detected with DAPI staining. HS induced a strong positive TUNEL staining selectively in DG and CA1 KO-Tau neurons. The arrows indicate TUNEL-positive neurons. As a positive control, DG and CA1 sagittal sections from 7-month-old WT mice in control condition have been pretreated with a low concentration of DNAse to create substrate for the end-labeling reaction. The scale bars indicate 20 µm. (C) The effect of Tau deficiency on nuclear nucleic acid integrity was detected using the TUNEL assay under C, HS or HS+24 h conditions. The level of gray (0 = black; 255 = white) was quantified within the nuclei (based on DAPI detection) in cells from whole WT hippocampi (HIP) or DG and CA1 subfields from KO-Tau hippocampi. Tau deficiency clearly increased the averaged gray levels in the DG and CA1 regions in C and HS conditions. 24 h after HS, the gray level fully returned to basal levels in the nuclei from KO-Tau DG neurons but only partially decreased in the CA1 neurons, which shows the selective weakness of CA1 neurons compared with DG cells in the removal of HS-induced damage. The data shown are the mean ± S.D. of 20–30 nuclei. *** p < 0.001; * p < 0.05. (D) Quantification of DAPI-stained nuclei did not show significant changes in cell density in 7-month-old CA1 KO-Tau mice after HS or HS+24 h. These data indicate that HS-generated nucleic acid damage did not promote cell death.