Fig. 1.
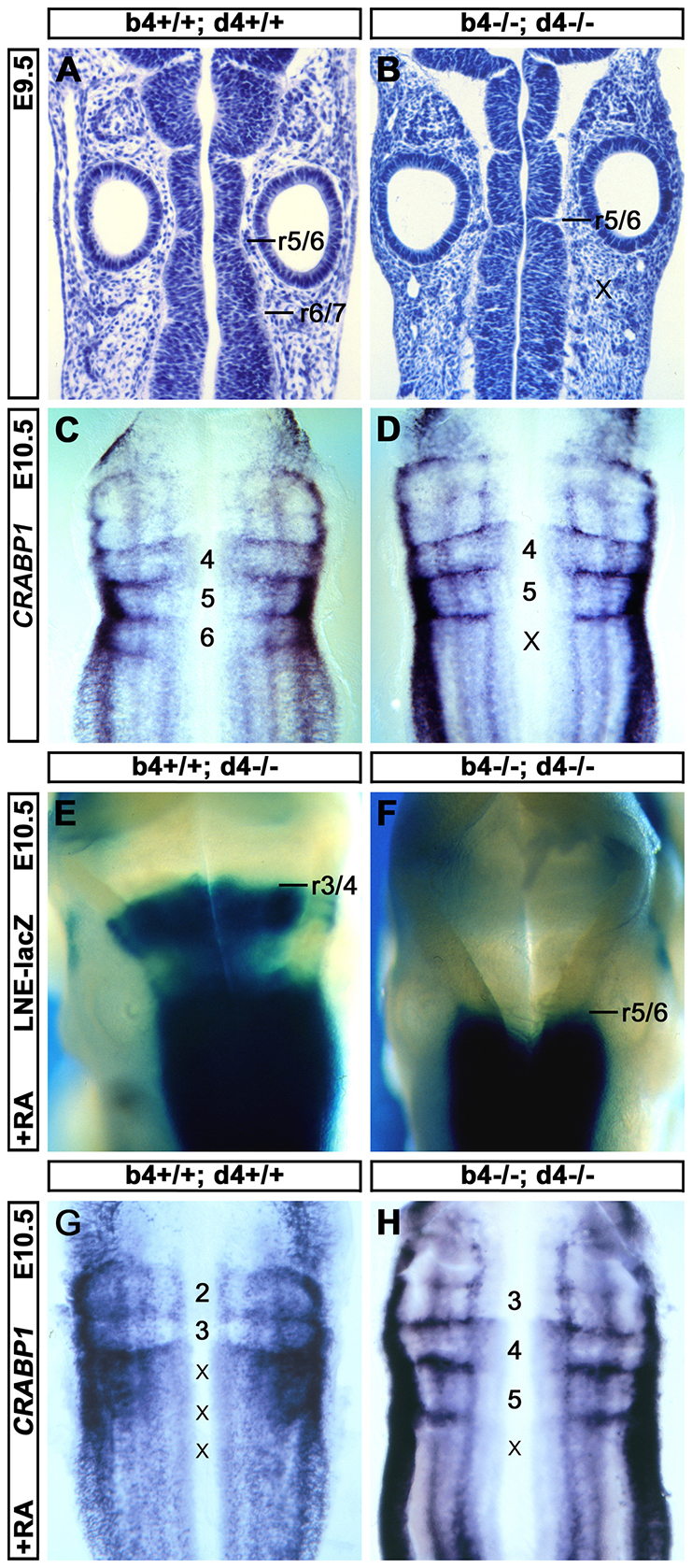
Hox4 genes are required for the mouse r6/r7 boundary. (A,B) Hematoxylin-stained coronal sections of E9.5 mouse hindbrains showing a visible r6/r7 boundary in wild-type (A) but not in Hoxb4-/-; Hoxd4-/- (B) embryos. Positions of posterior rhombomere boundaries (r5/r6, r6/r7) and the presumptive missing r6/r7 boundary (x) are indicated. (C,D) Flat-mounted E10.5 mouse hindbrains showing enrichment of Crabp1 mRNA at rhombomere boundaries in wild-type (C) and in Hoxb4-/-; Hoxd4-/- (D) embryos. The positions of rhombomeres and mispecified r7 (x) are indicated. (E,F) Dorsal views of the hindbrains of E10.5 mouse embryos expressing an LNE-LacZ reporter (blue staining) in a Hoxb4+/+; Hoxd4-/- (E) or Hoxb4-/-; Hoxd4-/- (F) genetic background after RA treatment at E9.25. The rhombomere boundaries corresponding to the anterior limit of LacZ staining (indicating the anterior limit of posterior Hox gene misexpression) are indicated. (G,H) Flat-mounted E10.5 mouse hindbrains showing Crabp1 mRNA after RA treatment at E9.25 in wild-type (G) and in Hoxb4-/-; Hoxd4-/- (H) embryos. Rhombomeres retaining clearly discernible Crabp1 boundary expression are numbered and those with disrupted boundary expression are indicated with a cross.
