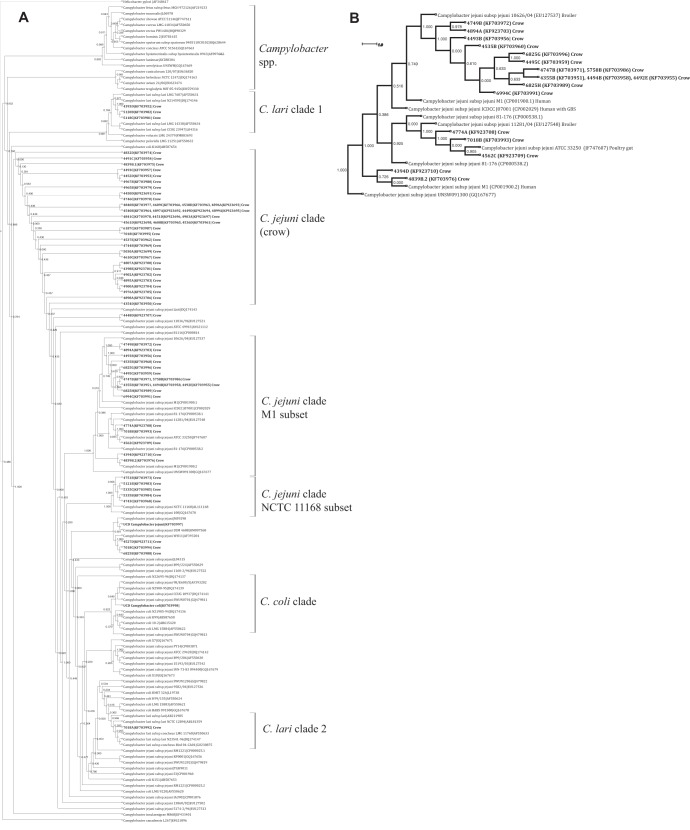
FIG 1.
16S rRNA phylogenetic analysis. (A) Annotated cladogram depicting relationships between the total Campylobacter isolates collected from American crows in this study and other known Campylobacter isolates. The tree is rooted to Helicobacter pylori. Campylobacter isolates from crows are indicated in bold. The species, strain, and accession number are listed for each publicly accessible sequence. The cluster corresponding to “Campylobacter spp.” contains non-C. jejuni Campylobacter sequences, including C. avium, C. rectus, and C. fetus along with the H. pylori root. Other clades are defined in the text. (B) Expanded phylogram depicting crow isolates clustered around known C. jejuni isolates, some of human origin (strain M1). Numbers at nodes are FastTree local support values based on the Shimodaira-Hasegawa (SH) test, where 1.000 represents the strongest relationship and 0.000 indicates low support. Distance is indicated by a scale bar.