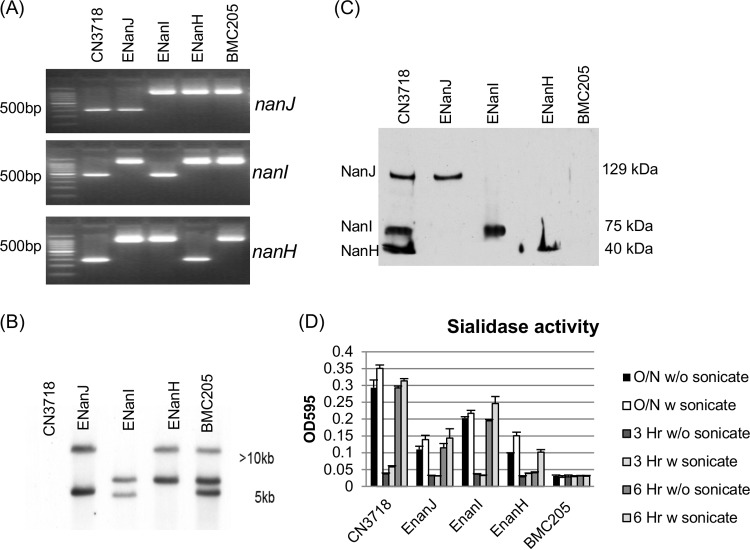
FIG 1.
Intron-based insertional mutagenesis to create CN3718 mutants that express only NanJ, NanI, or NanH sialidase. (A) Internal nanJ-, nanI-, and nanH-specific PCR results for wild-type CN3718, ENanJ (expressing only NanJ), ENanI (expressing only NanI), and ENanH (expressing only NanH). Also shown is BMC205, a nanJ nanI nanH triple null mutant strain that had been constructed previously (17). Using DNA from wild-type strain CN3718, a PCR specific for nanJ, nanI, or nanH sequences amplified the expected PCR products of 306 bp for nanJ, 467 bp for nanI, and 285 bp for nanH. The same primers amplified PCR products of ∼1,200 bp, ∼1,400 bp, and ∼1,200 bp using DNA from mutants whose nanJ, nanI, or nanH gene had been targeted for the insertion of an ∼900-bp intron. The migration of 100-bp DNA markers is shown on the left. (B) Southern blot analysis of wild-type CN3718 or the ENanJ, ENanI, ENanH, and BMC205 mutant strains using an intron-specific DIG-labeled probe. DNA size markers are shown on the right. (C) Sialidase Western blot analysis of sialidase expression of wild-type CN3718, ENanJ, ENanI, ENanH, and BMC205 null mutant strains in TH 16-h culture supernatants. Protein size markers are shown on the right. Wild-type CN3718 expresses all three sialidases, including NanJ (129 kDa), NanI (77 kDa), and NanH (43 kDa). (D) Sialidase enzyme activity present after wild-type CN3718 or the ENanJ, ENanI, ENanH, and BMC205 mutant strains were grown for 3 h, 6 h, or 16 h with or without sonication. All experiments were repeated three times, and mean values are shown. The error bars indicate standard deviations.