FIG 7.
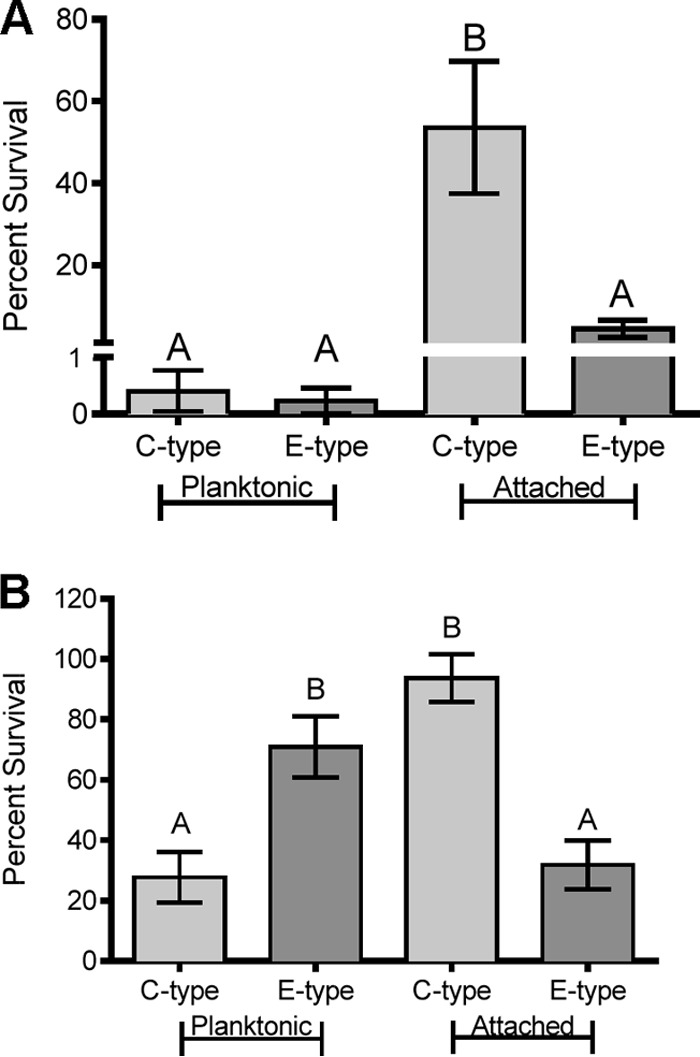
(A) Protective effect of chitin attachment upon exposure to acid stress. Depicted is the survival of two C-genotype strains (CMCP6 and M06-24) and two E-genotype strains (ENV1 and JY1305) when exposed to acid stress (pH 3) for 5 min in the planktonic state or when attached to chitin. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means for four replicates of two strains. Different letters indicate significant differences determined by using one-way ANOVA. Attachment to chitin provided a significant protective effect against acid stress for C-genotype strains only. (B) Effect of chitin attachment on exposure to bile stress. Depicted is the survival of two C-genotype strains (CMCP6 and M06-24) and two E-genotype strains (ENV1 and JY1305) when exposed to 1% bile for 30 min in the planktonic state or when attached to chitin. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means for two (planktonic) or four (attached) replicates of two strains. Different letters indicate significant differences determined by using one-way ANOVA. E-genotype strains survived bile stress significantly better than did C-genotype strains when in the planktonic state, while C-genotype strains survived bile stress significantly better than did E-genotype strains when attached to chitin.
