FIG 6.
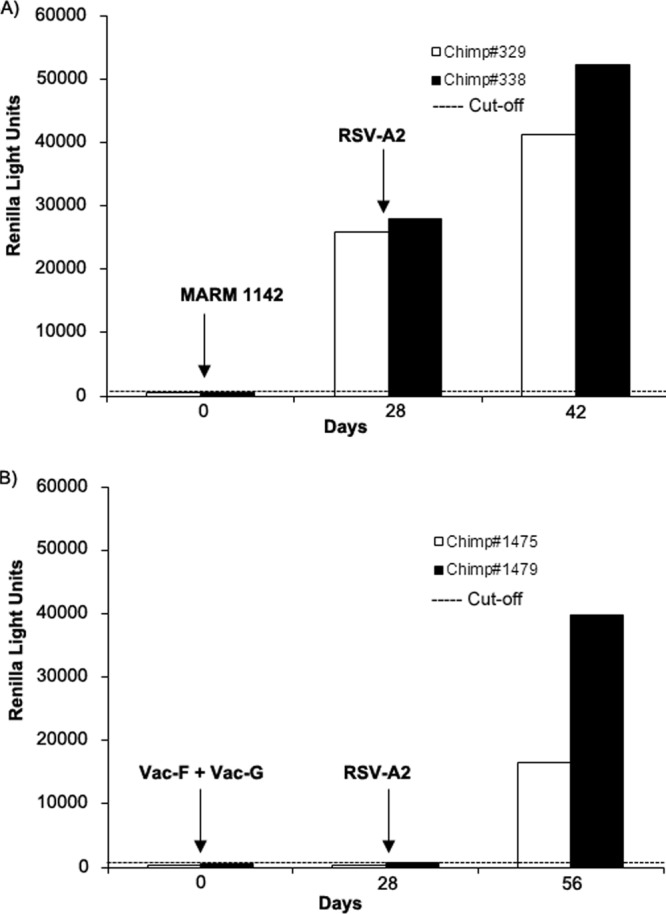
Two groups of chimpanzees (group 1, chimps no. 329 and 338; group 2, chimps no. 1,475 and 1,479) were immunized with live RSV-MARM-1142 by combined intranasal/intratracheal installation or inoculated with vaccinia-RSV-F and vaccinia-RSV-G viruses, respectively, and then challenged with live RSV-A2 using combined intranasal/intratracheal installation of the virus. Preimmune, postimmunization, and postchallenge antisera were tested for anti-RSV-N-specific IgG antibodies using the LIPS-NRSV assay. (A) Group 1 chimps were seronegative prior to immunization but showed a positive anti-RSV-N IgG response following administration of RSV-MARM-1142 and had a boost in the IgG response following infection with RSV-A2. (B) Group 2 chimps were seronegative prior to immunization and showed no anti-RSV-N-specific IgG antibody response following inoculation with vaccinia-RSV-F and vaccinia-RSV-G viruses. However, anti-RSV-N IgG responses were detected following challenge with RSV-A2.
