FIG 3.
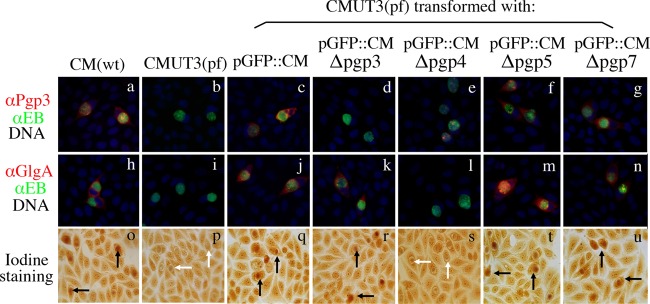
Effect of pORF deletion on Pgp3 and GlgA protein expression, as well as glycogen synthesis. The five stable transformants along with wild-type (wt) C. muridarum (CM) and plasmid-free (pf) CMUT3 organisms were used to infect HeLa cells. The infected cells were used for triple immunofluorescence labeling for Pgp3 (red, panels a to g) and GlgA (red, h to n) proteins, chlamydial organisms (green) and DNA (blue) and iodine staining of glycogen accumulation (o to u). Inclusions positive for glycogen staining were marked with black arrows, while inclusions lacked glycogen with white arrows. Note that both GlgA expression and glycogen accumulation were restored in CMUT3 transformed with pGFP::CM (panels j and q) and plasmids with deletion of pgp3 (panels k and r), pgp5 (panels m and t), or pgp7 (panels n and u) but not pgp4 (panels l and s). The Pgp3 protein was also significantly reduced in pgp4 deletion mutant (panel e).
