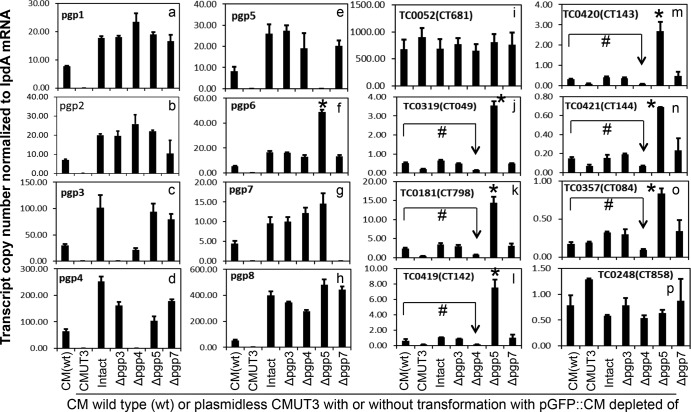
FIG 4.
Effect of pORF deletion on the expression of plasmid-encoded and -regulated genes. Wild-type (wt) C. muridarum and six plasmid-free C. muridarum organisms were used to infect HeLa cells. Cultures were harvested at 20 h postinfection for quantitative RT-PCR detection of transcripts of the eight plasmid-encoded (panels a to h) and eight genome-encoded (panels i to p) ORFs. The plasmid-free C. muridarum organisms were transformed without (CMUT3) or with pGFP::CM (Intact) or with deletion of pORFpgp3 (Δpgp3), pgp4 (Δpgp4), pgp5 (Δpgp5), and pgp7 (Δpgp7), respectively, as listed along the x axis. The transcript copy numbers normalized to lpdA mRNA for each of 16 measured ORFs are shown along the y axis. Note that pgp5 deletion significantly increased expression of pgp6 (panel f), TC0319 (homologue of CT049, panel j), TC0181 (homologue of CT798, panel k), TC0419 (homologue of CT142, panel l), TC0420 (homologue of CT143, panel m), TC0421 (homologue of CT144, panel n), and TC0357 (homologue of CT084, panel o). Stars (*) indicate a significant increase compared to transformants that carry the intact pGFP::CM, while “#” symbols indicate a significant decrease in gene expression compared to wild-type C. muridarum (CM). The transcript profiles were also compared after normalization with genome copies (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material), and similar results were obtained.