FIG 8.
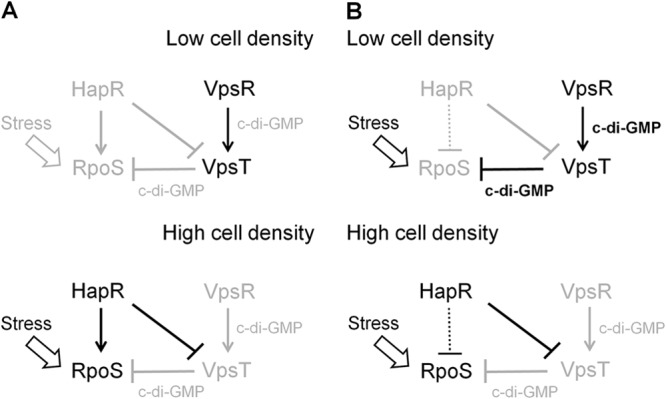
Model for the interplay between HapR and VpsT in the regulation of RpoS expression. Disabled regulations and low c-di-GMP content are represented by lines and fonts in light grayscale. Symbols: →, activation; ⊥, repression. (A) Planktonic cells. In nutrient-rich medium, the level of c-di-GMP is not sufficiently high for VpsT to repress rpoS transcription. HapR enhances rpoS in a VpsT-independent manner. (B) Biofilm cells. Biofilm cells can exhibit a higher starting intracellular c-di-GMP level than planktonic cells and experience stress conditions resulting in earlier expression of RpoS. At a low cell density, VpsT represses rpoS transcription. At a high cell density, HapR represses VpsT and diminishes the c-di-GMP pool to relieve rpoS from VpsT repression. We postulate that in biofilms, HapR could have a negative effect on rpoS expression (dotted line) that is masked in the hapR mutant due to the much stronger repressive effect of VpsT.
