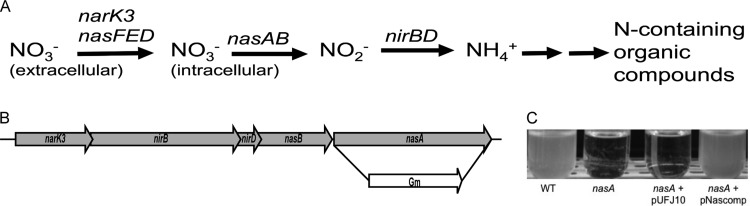
FIG 1.
Organization of the R. solanacearum nitrate assimilation pathway and its function in culture. (A) The nitrate assimilation pathway allows for the uptake of nitrate and reduction of both nitrate and nitrite for use in the synthesis of organic compounds. The relevant genes are listed above each enzymatic step. Annotations: narK3 and nasFED, nitrate uptake transporters; nasA, large catalytic subunit of the assimilatory nitrate reductase; nasB, small subunit of the assimilatory nitrate reductase; nirB, large catalytic subunit of the assimilatory nitrite reductase; nirD, small subunit of the assimilatory nitrite reductase. (B) The R. solanacearum nitrate assimilation operon and construction of the nasA mutant strain. The complete nasA ORF was replaced with a gentamicin resistance cassette, as shown. (C) Growth of R. solanacearum strains in minimal medium with 5 mM nitrate as the sole nitrogen source, imaged after 72 h. WT, wild-type R. solanacearum UW551; nasA, nasA deletion mutant; nasA + pUFJ10, nasA mutant plus empty vector; nasA + pNascomp, complemented nasA mutant.