FIG 7.
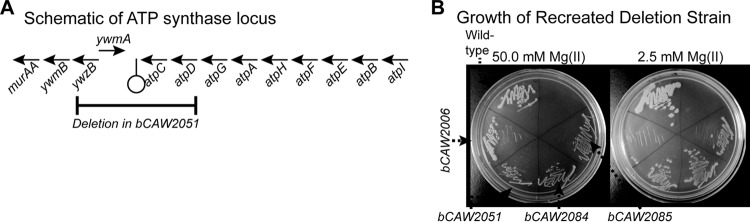
A genomic deletion near the ATP synthase locus is responsible for suppressing a defect in magnesium transport activity. (A) As shown in this schematic, the bCAW2051 suppressor mutant contains a large deletion that encompasses the last two genes of the atp operon as well as two neighboring genes, ywzB and ywmA. (B) To verify that the deletion at the atp locus was responsible for the bCAW2051 suppressor phenotype, the deletion was recreated in a clean bCAW2006 background strain, resulting in two identical strains, bCAW2084 and bCAW2085. Both of these mutants grew on media with lowered magnesium concentrations, in contrast to their background strain, bCAW2006, confirming a functional relationship between the deleted genes and the suppressor phenotype.
