FIG 3.
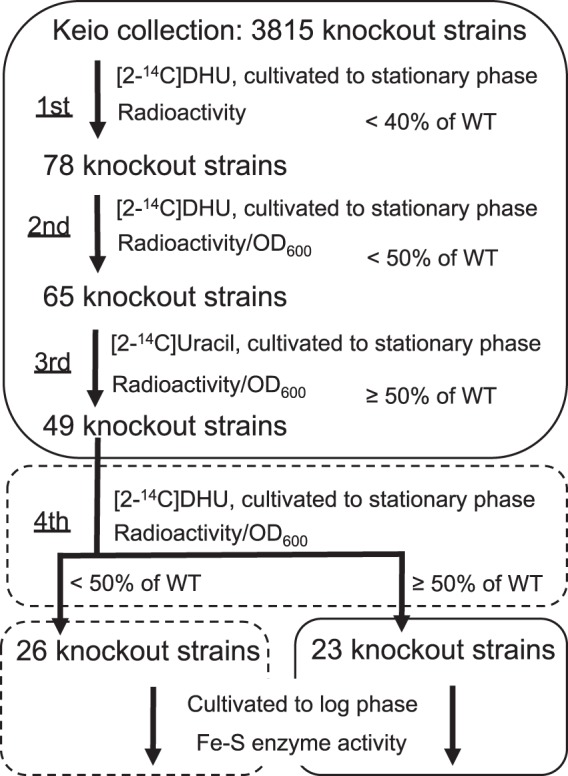
The screening procedure and summary of identification of the genes affecting Fe-S biogenesis and iron homeostasis. In the first screening step, knockout strains whose radioactivity (14C cpm) was less than 40% of that of the wild-type (WT) strain were selected. In the second screen, knockout strains whose radioactivity (14C cpm · OD600−1) was less than 50% of the wild-type level were selected. In the third screening step, knockout strains exhibiting radioactivity less than half of that of the wild-type strain were excluded. In the fourth step, each strain was aerobically cultivated with shaking in LB medium containing [2-14C]DHU. After the fourth step, each of the 26 knockout strains whose radioactivity was less than half of that of the wild-type strain was aerobically cultivated in LB broth with shaking, while each of the 23 knockout strains exhibiting radioactivity more than half of the wild-type strain was statically cultivated in LB medium for Fe-S enzyme assays. The boxes with the solid and broken lines indicate that the cultivations were carried out microaerobically with static culture and aerobically with shaking, respectively.
