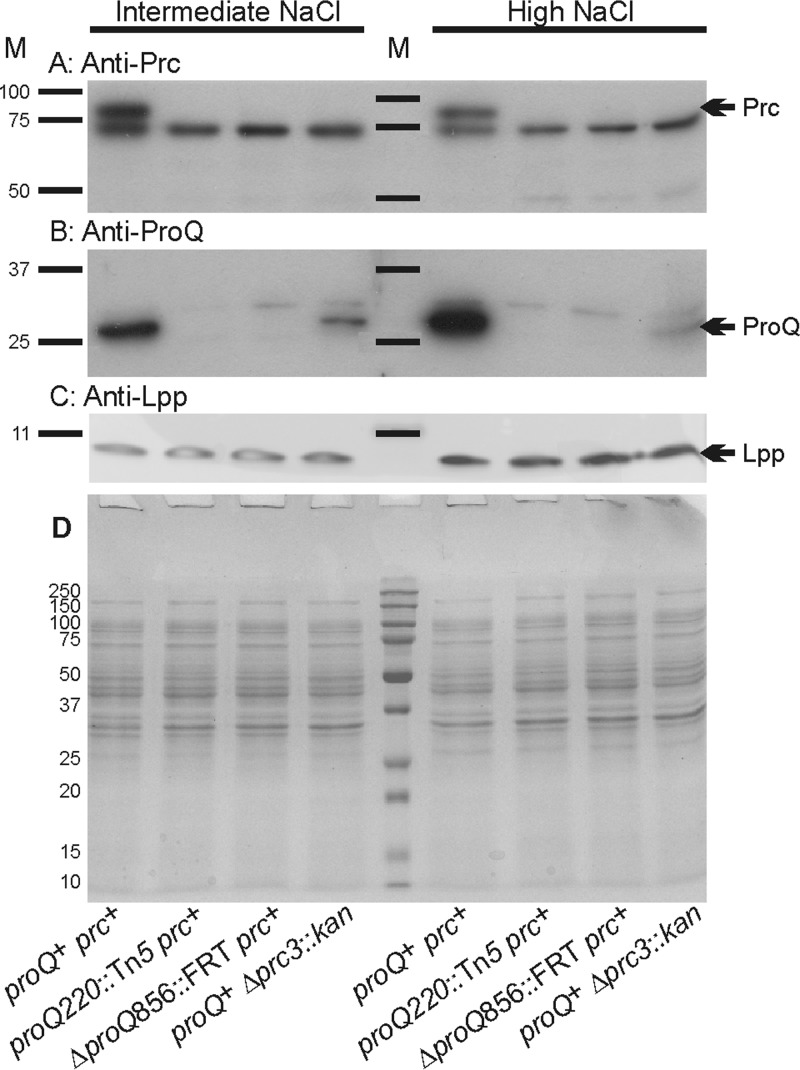
FIG 4.
Impacts of proQ and prc lesions on Prc, ProQ, and Lpp protein levels. E. coli strains RM2 (proQ+ prc+), WG174 (RM2 proQ220::Tn5 [phenotypically ProQ− Prc−]), WG1119 (RM2 ΔproQ856::FRT [phenotypically ProQ− Prc−]), and WG703 (RM2 Δprc3::kan [phenotypically ProQ+ Prc−]) were grown in MOPS medium supplemented with 120 mM NaCl (intermediate NaCl) or 250 mM NaCl (high NaCl). Aliquots of cell extracts containing 15 μg of protein were analyzed by Western blotting to detect Prc (A) or ProQ (B), and aliquots containing 1.5 μg of cell protein were analyzed to detect Lpp (C). In panel A, the band immediately below Prc, shared in all samples, represents a protein that is not related to Prc (M. Ehrmann, personal communication). Panel D shows a corresponding GelCode Blue-stained SDS-PAGE gel. M, molecular weight markers; arrows, locations of Prc, ProQ, and Lpp.