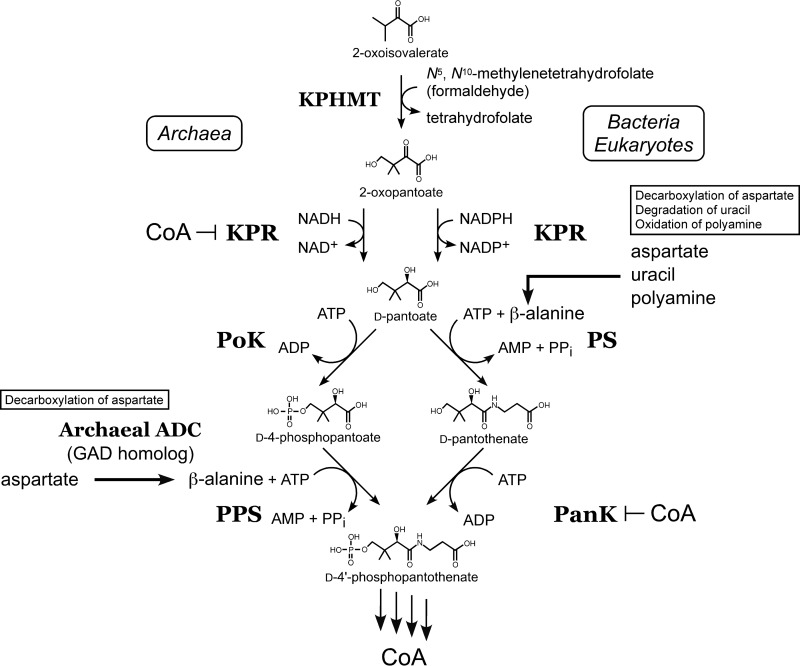
FIG 7.
Diagram illustrating the first four enzyme reactions in CoA biosynthesis in T. kodakarensis in comparison with those in bacteria and eukaryotes. The first four enzyme reactions of the archaeal CoA biosynthesis pathway in T. kodakarensis, catalyzed by KPHMT, KPR, PoK, and PPS, are shown on the left. Inhibition of archaeal KPR and bacterial/eukaryotic PanK by CoA is indicated. In bacteria and eukaryotes, β-alanine is synthesized by either the direct decarboxylation of Asp, the degradation of uracil, or the oxidation of polyamines. In archaea, β-alanine is synthesized by the archaeal ADC identified in this study, which is a GAD homolog.