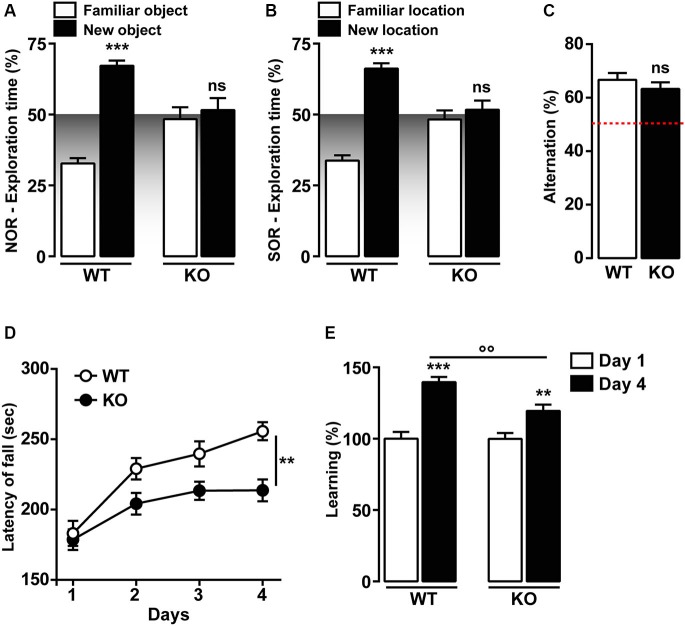
Figure 3.
Memory functions in Cav3.2 deficient mice. (A) Graph shows the percentage of exploration time of Cav3.2 KO (n = 14) and WT (n = 15) mice in the NOR test. Data (means ± SEM) were analyzed using two-way ANOVA: (Object exploration × Genotype: F(1, 44) = 25.80, P < 0.0001; Object exploration: F(1, 44) = 37.58, P < 0.0001; Genotype: F(1, 44) = 3.245e-014, P = 0.99). Specific comparisons: *** p < 0.001 (WT-new vs. WT-familiar). (B) Graph shows the percentage of exploration time of Cav3.2 KO (n = 14) and WT (n = 15) mice in the SOR test. Data (means ± SEM) were analyzed using two-way ANOVA: (Object exploration × Genotype: F(1, 44) = 31.80, P < 0.0001; Object exploration: F(1, 44) = 48.81, P < 0.0001; Genotype: F(1, 44) = 1.324e-013, P = 0.99). Specific comparisons: *** p < 0.001 (WT-new vs. WT-familiar). (C) Histogram indicates the percentage of spontaneous alternation of Cav3.2 KO (n = 14) and WT (n = 15) in the Y-maze test. The red dotted line represents the chance level of alternation (random, 50%). Data (means ± SEM) were analyzed using Student’s t-test: ns. (D) Curves show coordination and motor learning in WT (n = 22) and Cav3.2 KO (n = 22) mice over a training period of 4 days. Data (means ± SEM) were analyzed using two-way ANOVA (Time × Genotype: F(3, 168) = 2.017, P = 0.1134; Time: F(3, 168) = 19.03, P < 0.0001; Genotype: F(1, 168) = 20.12, P < 0.0001). Specific comparisons: ** p < 0.01 (KO-Day4 vs. WT-Day4). (E) Percentage of motor learning in WT (n = 22) and Cav3.2 KO (n = 22). Data (means ± SEM) were analyzed using two-way ANOVA (Time × Genotype: F(1, 84) = 5.643, P < 0.05; Time: F(1, 84) = 5.654, P < 0.05; Genotype: F(1, 84) = 49.11, P < 0.0001). Specific comparisons: *** p < 0.001 (WT-Day4 vs. WT-Day1), ** p < 0.01 (KO-Day4 vs. KO-Day1) and °° p < 0.01 (KO-Day4 vs. WT-Day4).