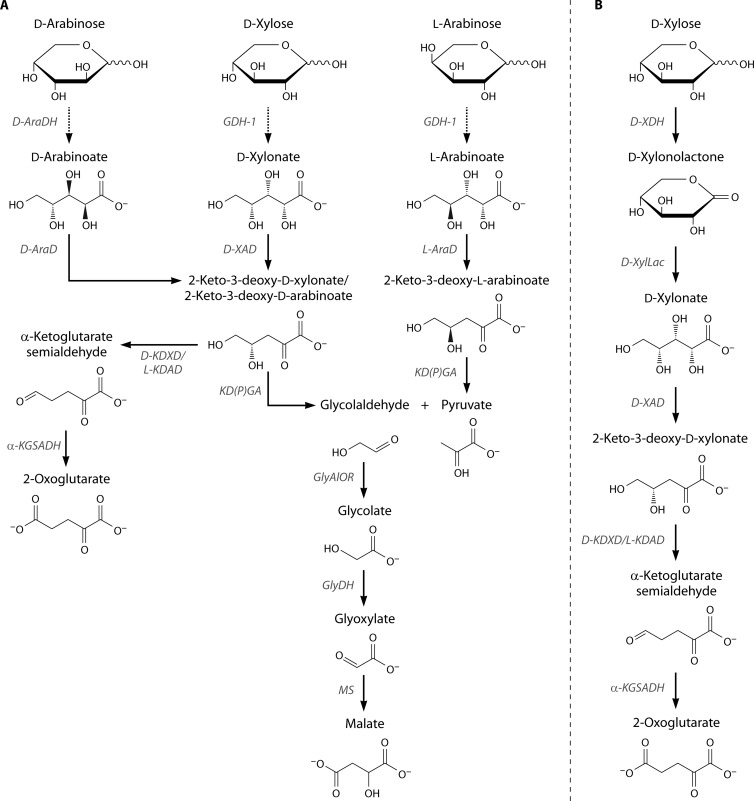
FIG 16.
Current understanding of pentose degradation pathways in Archaea. The degradation pathways reported for d-arabinose, d-xylose, and l-arabinose in Sulfolobus spp. (A) and the d-xylose degradation pathway in Haloferax volcanii (B) are depicted. The dashed arrow indicates the presence of lactones as intermediates, which are supposed to be spontaneously transformed to the respective sugar acid at high temperatures. AraDH, d-arabinose dehydrogenase; AraD, d-arabinoate dehydratase; α-KGSADH, α-ketoglutarate semialdehyde dehydrogenase; GDH-1, glucose dehydrogenase (isoenzyme 1) (SSO3003); GlyAlOR, glycolaldehyde:ferredoxin oxidoreductase; GlyDH, glycolate dehydrogenase; KD(P)G aldolase, 2-keto-3-deoxy-(6-phospho)gluconate aldolase; KDAD, 2-keto-3-deoxyarabinoate dehydratase; MS, malate synthase; KDXD, 2-keto-3-deoxyxylonate dehydratase; XDH, xylose dehydrogenase; XylLac, xylono-1,4-lactone lactonase; d-XAD, xylonate dehydratase.