Figure 5.
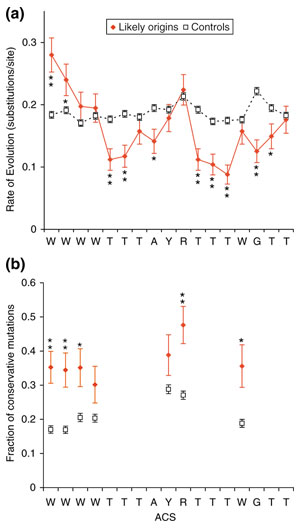
Conservation of the ACS across species. (a) The rate of evolution was calculated for the ACSs of 75 experimentally supported predictions and known origins (red solid diamonds, solid lines) using alignments to sequence of four other yeasts (see text). As a control, we performed the same analysis on 1,580 alignments of ACSs that passed the non-T step of Oriscan but did not match an ORC/MCM or known origin locus (black open squares, dashed lines). Substitutions per site were estimated by maximum parsimony, and error bars indicate the standard error of a Poisson distribution. Statistical significance is indicated by asterisks (* indicates p < 0.02; ** indicates p < 0.001). (b) The fraction of mutations that were conservative, that is, between the two allowed bases at a degenerate position, was calculated for each degenerate nucleotide of the ACS using the same probable active and control ACS alignments as in (a). Symbols and asterisks are as in (a).
