TABLE 2.
Lead optimization toward KAI407a
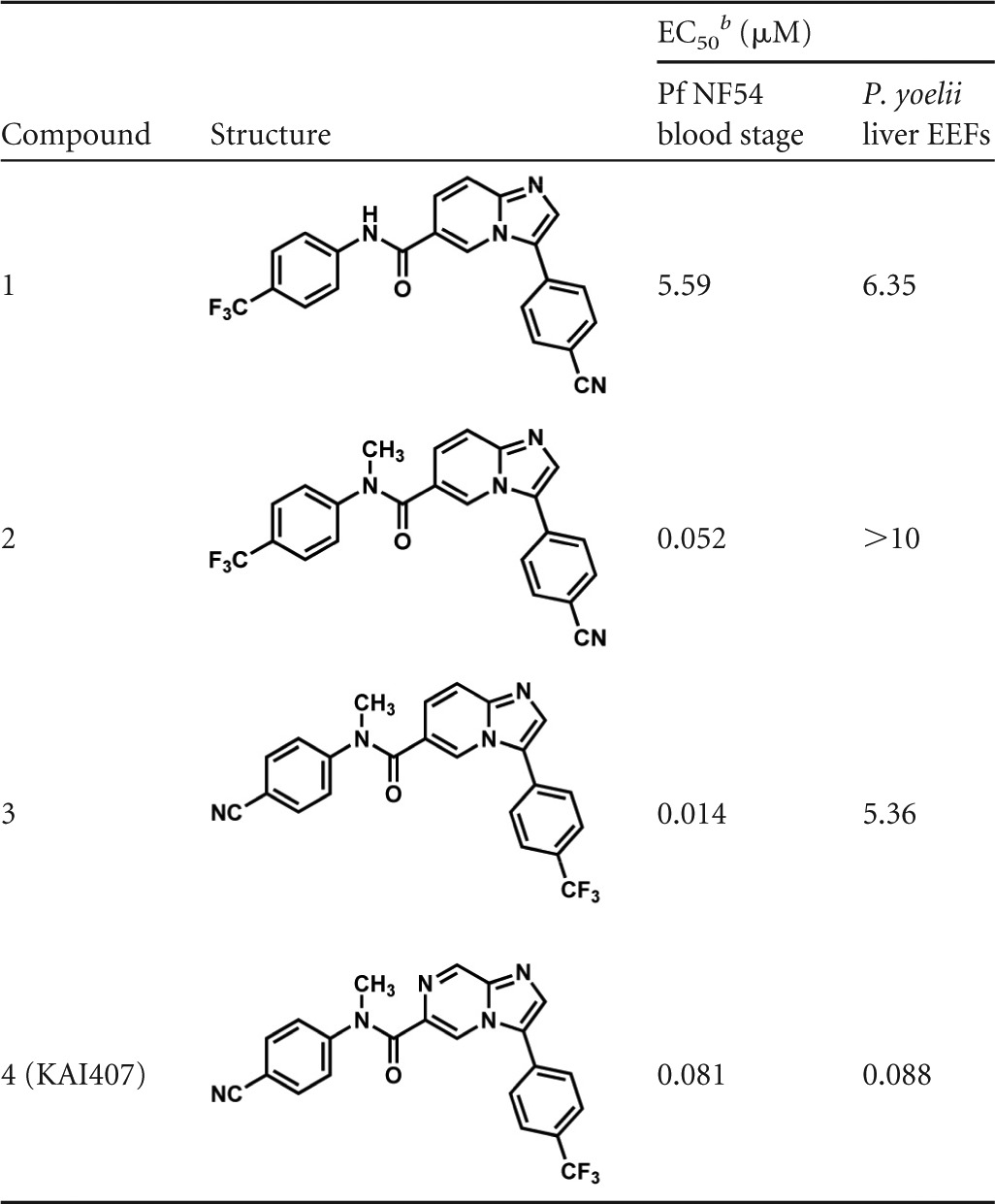
KAI407 was derived from lead compound 1, identified in a high-throughput blood stage screen, which also showed weak activity in an in vitro assay using P. yoelii sporozoites and HepG2 cells. Introduction of a methyl group to the amide nitrogen provided compound 2 and improved blood stage activity nearly 100-fold, but lost liver stage activity. By modification of both aryl appendages, we obtained compound 3, with blood and liver stage activity. Chemical modifications of the 6,5-heterocyclic core by introducing a nitrogen to the 5 position of the bicyclic core generated the imidazolopyrazine KAI407 (compound 4) with good potency (IC50 < 100 nM) on both blood and liver stage parasites.
EC50, 50% effective concentration.
