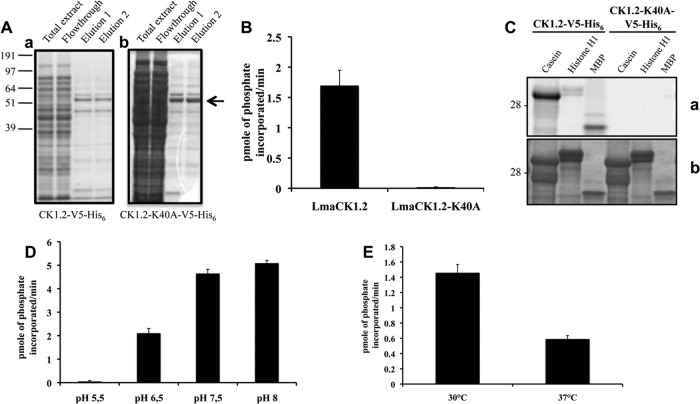
FIG 2.
LmaCK1.2, but not LmaCK1.2-K40A, strongly phosphorylates CK1 substrates. (A) Purification of LmaCK1.2 (a) and LmaCK1.2-K40A (b) from E. coli. Aliquots from the total extract, flowthrough, and two elutions from both samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, and the gel was stained by colloidal Coomassie (Bio-Rad). (B) Kinase assays were performed using 27 μM CK-S peptide and 0.5 μg of recombinant LmaCK1.2 or 1 μg of LmaCK1.2-K40A. The reaction samples were spotted onto P81 phosphocellulose paper (Whatman), and phosphate incorporation was measured using a scintillation counter. (C) Kinase assays were performed with 36 μg dephosphorylated casein 16 μg histone H1 or 6 μg MBP with 0.5 μg of recombinant LmaCK1.2 or 1 μg of LmaCK1.2-K40A. (a) Autoradiography; (b) Coomassie-stained gel. (D) One microgram of LmaCK1.2 was subjected to kinase assays at 30°C under increasing pH conditions, using 27 μM CK-S as the substrate. The reaction mixtures were spotted onto P81 paper, and the incorporated radioactivity was measured by a scintillation counter. (E) Recombinant LmaCK1.2 was subjected to kinase assays, as described for panel D, at pH 7.5 and either 30 or 37°C.