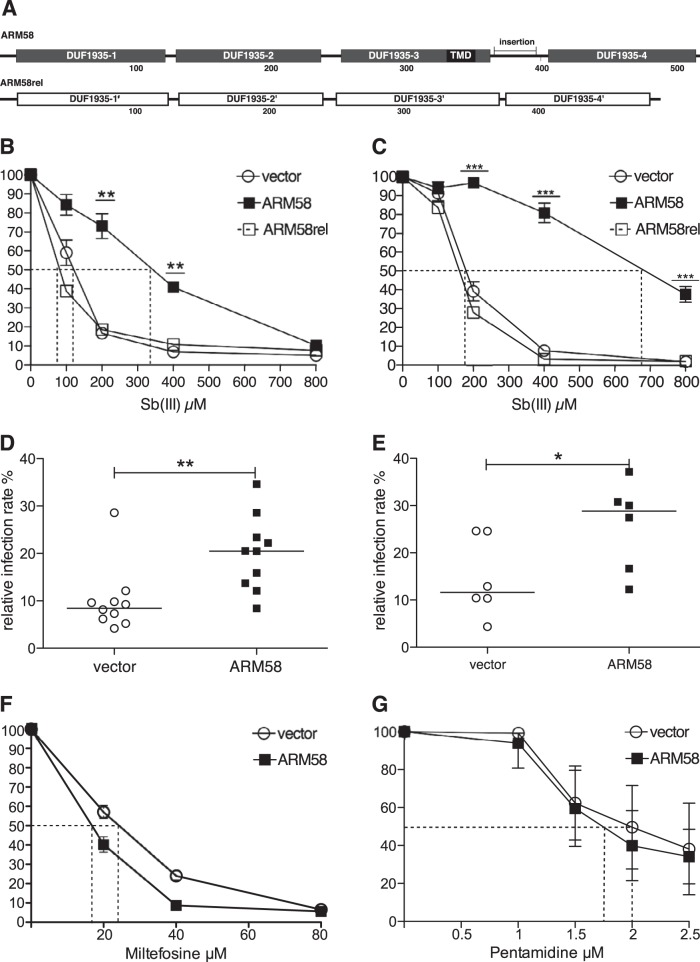
FIG 1.
Validation of LinARM58. (A) Putative domain structure of LinARM58 and LinARM58rel. The boxes represent 4 putative domains of unknown function (DUF1935) for each protein. TMD, transmembrane domain; insertion, 31-amino-acid sequence absent from ARM58rel. The numbers below the structures show the positions within the amino acid sequence. (B) Dose-inhibition experiment for growth of L. infantum carrying the indicated transgenes at the indicated antimonyl tartrate (SbIII) concentrations. Growth over 72 h was normalized to that of the 0 μM samples (100%). The dotted lines indicate the respective IC50s. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (n = 8). (C) As for panel B, but with L. donovani 1SR as the acceptor strain. (D) In vitro infection of bone marrow-derived macrophages and treatment with sodium stibogluconate. L. infantum transfected with vector or with the ARM58 transgene was used to infect BMMs at a 10:1 ratio. After 4 h, extracellular parasites were removed. Sodium stibogluconate was added to the cultures at 160 μg/ml, and incubation was continued for 72 h. After DAPI staining, infection rates relative to the untreated control infections (data not shown) were determined by fluorescence microscopy (10 experiments with 100 macrophages each). The horizontal bars depict the median values. **, P < 0.01. (E) As for panel D, except that L. donovani 1SR served as the acceptor strain. *, P < 0.05 (n = 6). (F) As for panel B, except that parasites were treated with the indicated concentrations of miltefosine. (G) As for panel B, except that parasites were treated with the indicated concentrations of pentamidine.