FIG 2.
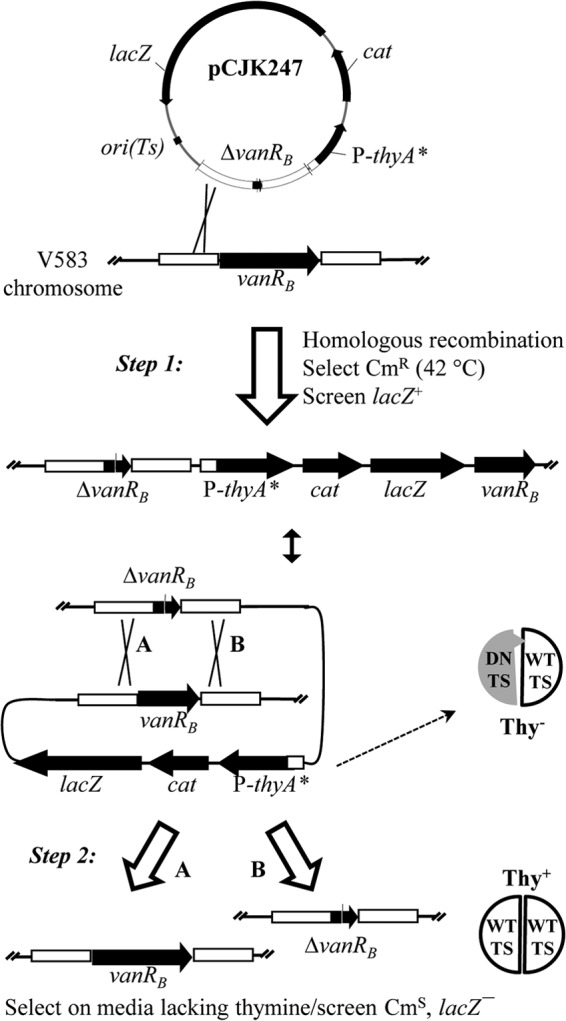
Schematic of dominant-negative TS-mediated genetic exchange. A derivative of pCJK245 carrying an allele of interest (e.g., pCJK247) is introduced into the target strain at a permissive temperature (30°C). Selection for resistance to Cm at a nonpermissive temperature (42°C) yields recombinants in which the plasmid has integrated into the chromosome via a region of cloned chromosomal DNA (step 1). Production of dominant-negative TS (DN TS) renders the cells Thy negative (Thy−) by interfering with wild-type TS (WT TS) activity. Plasmid excision (step 2) leaves either the wild-type allele (A) or the mutant allele (B) on the chromosome and renders the cells Thy+ (capable of robust growth on medium lacking thymine). An equivalent sequence of events can be drawn for plasmid integration at either the upstream or downstream fragment.
