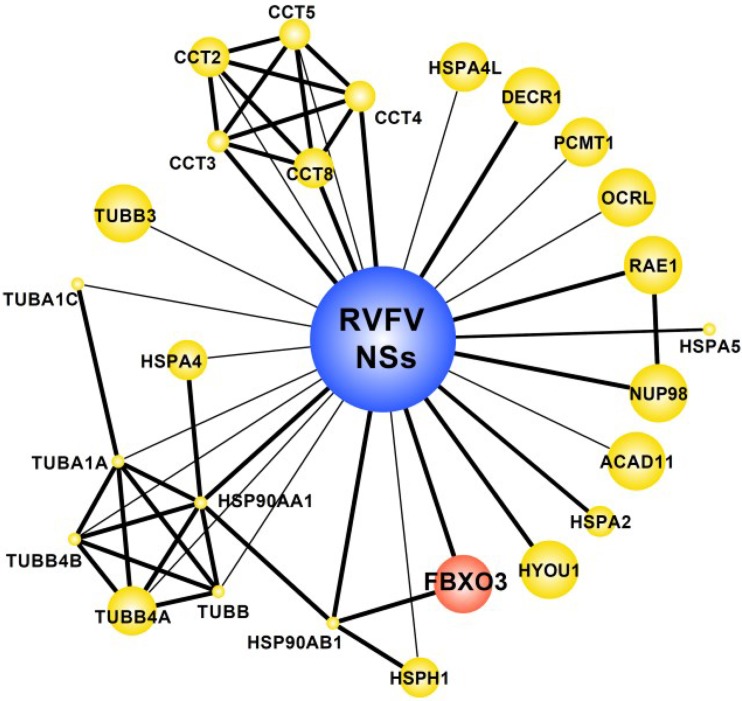
FIG 2.
Host cell interactors of RVFV NSs. Interactors of RVFV NSs protein were identified by affinity purification followed by mass spectrometry (AP-MS) using RVFV NSs as bait and as published in reference 22. Network representation shows interactions between NSs and AP-MS identified proteins (preys). Known direct protein interactions between preys are also shown (22). The edge thickness represents the number of spectra identified in the RVFV NSs precipitates (1, thin edge; >1, thick edge). The size of the symbols (nodes) indirectly correlates with numbers of identifications in the published data set, i.e., big symbols show proteins uniquely identified in RVFV NSs precipitates, whereas smaller symbols indicate identification with RVFV NSs as well as other (non-NSs) viral open reading frames. Red, presence of domains suggesting involvement in ubiquitin-dependent degradation (i.e., RING or FBX domains) based on SMART domain annotations; yellow, all other proteins.