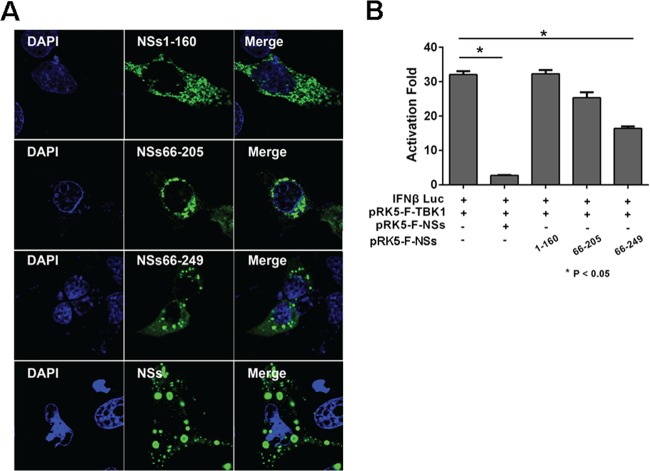
FIG 10.
The C-terminal region of NSs contributed to IB formation and IFN suppression. (A) HeLa cells were transfected with pRK5-NSs1-160, pRK5-NSs66-205, pRK5-NSs66-249, or pRK5-F-NSs. The cells were fixed and permeabilized 28 h posttransfection. Expression of various lengths of NSs and the formation of the IBs were shown by staining with anti-NSs antibodies and detected by immunofluorescence. (B) Full-length and truncated NSs exhibited distinct abilities of inhibiting IFN-β promoter activity. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing full-length and truncated NSs along with pGL3-IFN-β-Luc and pRL8 for 24 h, followed by stimulation with 50 μg/ml of poly(I · C) for another 8 h. Cell lysates were prepared and measured for luciferase activities. The experiments were repeated at least three times, and the data from one representative experiment with two technical repeats were presented.