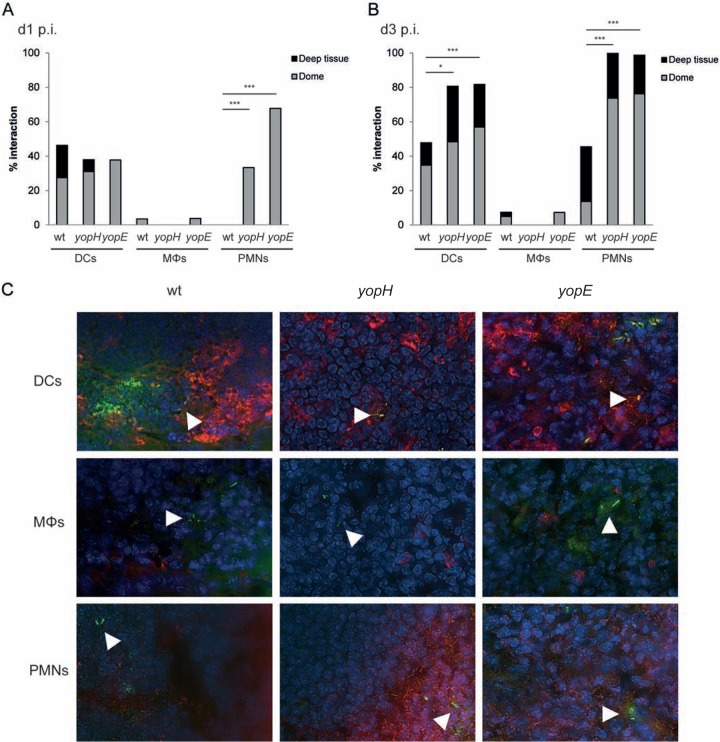
FIG 1.
Avirulent Yop mutants, but not wild-type Y. pseudotuberculosis, interact with PMNs during early infection. BALB/c mice were infected with wt bioluminescent Y. pseudotuberculosis or a yopH or yopE mutant. At 1 and 3 days postinfection, ceca positive for bacterial signals by IVIS were collected. Tissues were cryosectioned and were stained for bacteria in combination with staining for dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages (Mϕs), or neutrophils (PMNs). Stained ceca were analyzed by microscopy, and each bacterium observed was calculated as one event. Bacterial foci were not included in the analysis. (A) Percentage of bacteria interacting with immune cells in the subepithelial dome and the whole lymphoid follicle at day 1 (d1) p.i. Data for wt Y. pseudotuberculosis represent 15 sections per staining from 7 to 8 mice; data for the yopH mutant represent 16 to 21 sections per staining from 8 to 10 mice; and data for the yopE mutant represent 12 to 20 sections per staining from 4 to 7 mice. Differences between groups were analyzed by Fisher's test, with significance set at P values of <0.05 (*), <0.01 (**), or <0.001 (***). (B) Percentage of bacteria interacting with immune cells in the subepithelial dome and the whole lymphoid follicle at day 3 p.i. Data for wt Y. pseudotuberculosis represent 8 to 11 sections per staining from 4 to 5 mice; data for the yopH mutant represent 7 to 9 sections per staining from 4 mice; and data for the yopE mutant represent 4 to 5 sections per staining from 4 to 5 mice. (C) Representative images of bacteria interacting (or not) with DCs, Mϕs, or PMNs in lymphoid follicles of the cecum at day 1 p.i. White arrowheads indicate single bacteria.