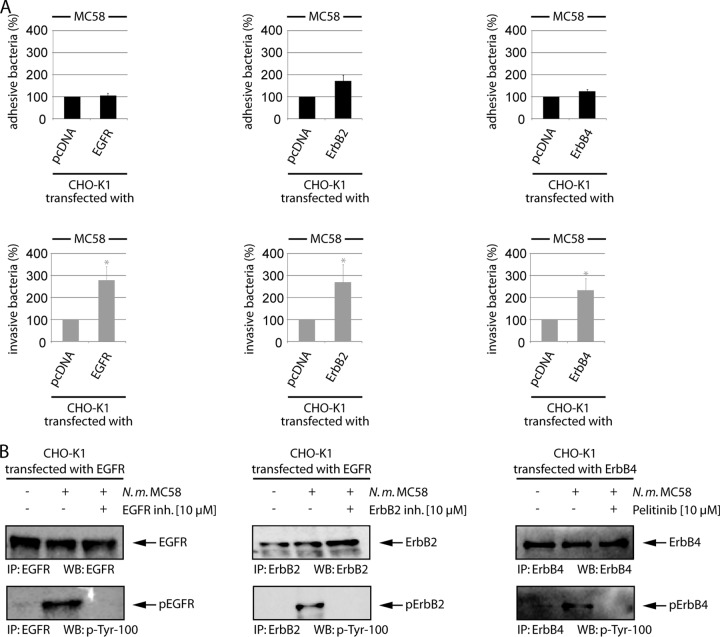
FIG 5.
Heterologous expression of EGFR, ErbB2, and ErbB4 results in increased bacterial uptake. (A) CHO-K1 cells were transfected with control plasmid or 1 μg mammalian expression vector encoding EGFR, ErbB2, or ErbB4, and cells were infected with strain MC58. Percentages of adherent (black bars) and invasive (gray bars) bacteria were determined. Percentages of adhesion and invasion for ErbB-transfected cells were compared to results with pcDNA-transfected cells. The data are means ± SD of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. (B) In parallel, ErB receptors were immunoprecipitated from infected cell lysates (IP), and samples were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-EGFR, anti-ErbB2, and anti-ErbB4 antibodies (upper panel). Following stripping, the blots were reprobed with p-Tyr-100 antibody (lower panel). In addition, cells were preincubated with the ErbB inhibitors EGFR inhibitor II (BIBX1382), ErbB2 inhibitor II, or ErB1/2/4 inhibitor (Pelitinib; EKB-569).