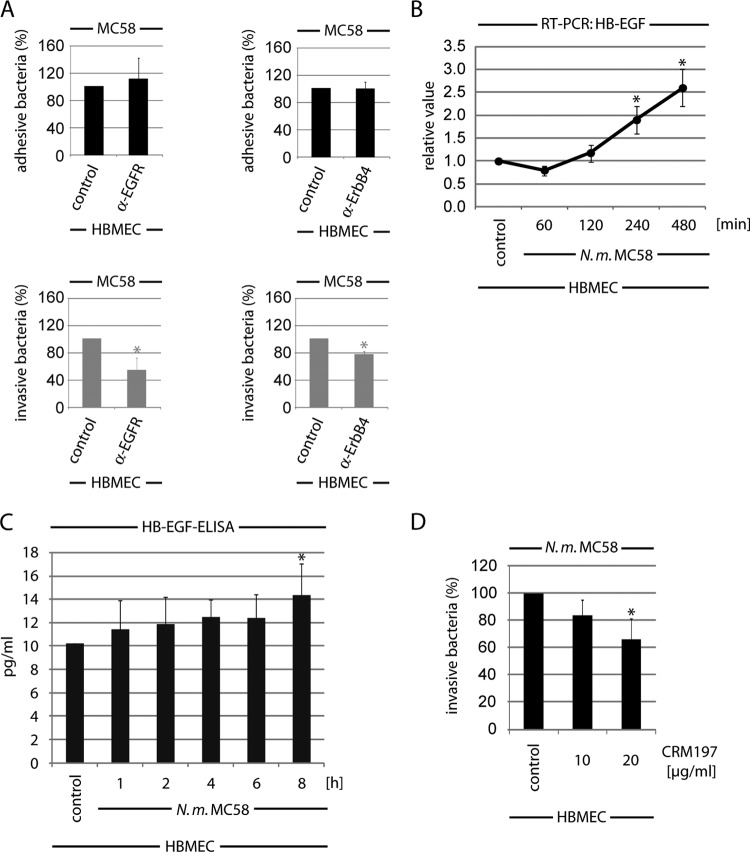
FIG 6.
ErbB activation follows HB-EGF release during infection. (A) HBMEC were incubated with neutralization antibodies against EGFR or ErbB4 (each at 5 μg/ml), respectively, for 1 h and then infected with MC58. Adhesive and invasive bacteria were determined in a gentamicin protection assay as described above. Percentages of adhesion and invasion of untreated cells were compared to results with antibody-treated cells. *, P < 0.05. (B) HB-EGF mRNA levels in HBMEC infected with N. meningitidis. HBMEC were infected with N. meningitidis MC58 or left uninfected (control). mRNAs were extracted at the indicated time points of infection, and quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR was performed. Target gene, HB-EGF; reference gene, GAPDH. Means and SD were calculated from the results of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (C) Estimation of released HB-EGF after infection of HBMEC with MC58. At the indicated time points, membrane-bound HB-EGF was dissolved by washing with 1.5 M NaCl–PBS–1% BSA, and the HB-EGF concentration was quantified in a commercial HB-EGF ELISA. (D) HBMEC were pretreated with the HB-EGF inhibitor CRM197 and infected with N. meningitidis MC58, and percentages of intracellular bacteria were determined after a further 4-h incubation. Means and SD results are from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. *, P < 0.05, relative to untreated cells.