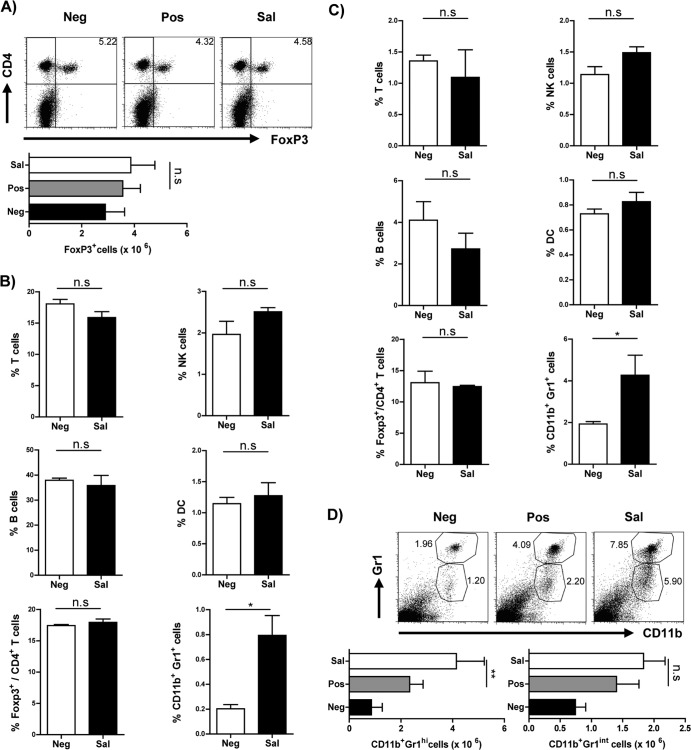
FIG 3.
Alteration of cellular compartment upon S. Typhimurium infection. (A) Representative FACS plots gated on live CD3+ lymphocytes and histograms indicate the frequency and the total numbers of CD4+ Foxp3+ Treg cells in the spleen of mice from the different groups used in the airway inflammation model. Histograms indicate the frequency of various cell populations, i.e., T cells (CD3+), B cells (CD19+), NK cells (CD49b+), conventional DCs (cDCs) (CD11c+ and major histocompatibility complex class II-positive [MHCII+]), Treg cells (Foxp3+), and myeloid cells (CD11b+ Gr1+), in the spleen (B) and lungs (C) of mice infected with S. Typhimurium (Sal) in contrast to uninfected mice (Neg). The frequencies of all cell types were determined from the total-live-cell gate. Foxp3+ cell frequency was determined from gating live CD3+ CD4+ lymphocytes. (D) Representative FACS plots and histograms indicate the frequencies and total numbers of CD11b+ Gr1hi and CD11b+ Gr1int myeloid cells in the spleen of mice from the different groups used in the airway inflammation model. These cell frequencies were ascertained from the total live-cell gate. In panels A and D, data are representative plots from three individual experiments with 4 to 6 mice per group. ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance. In panels B and C data are represented as means plus SD and are representative of two individual experiments with 3 to 4 mice per group. A Mann-Whitney test was used for determining statistical significance. n.s, nonsignificant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.