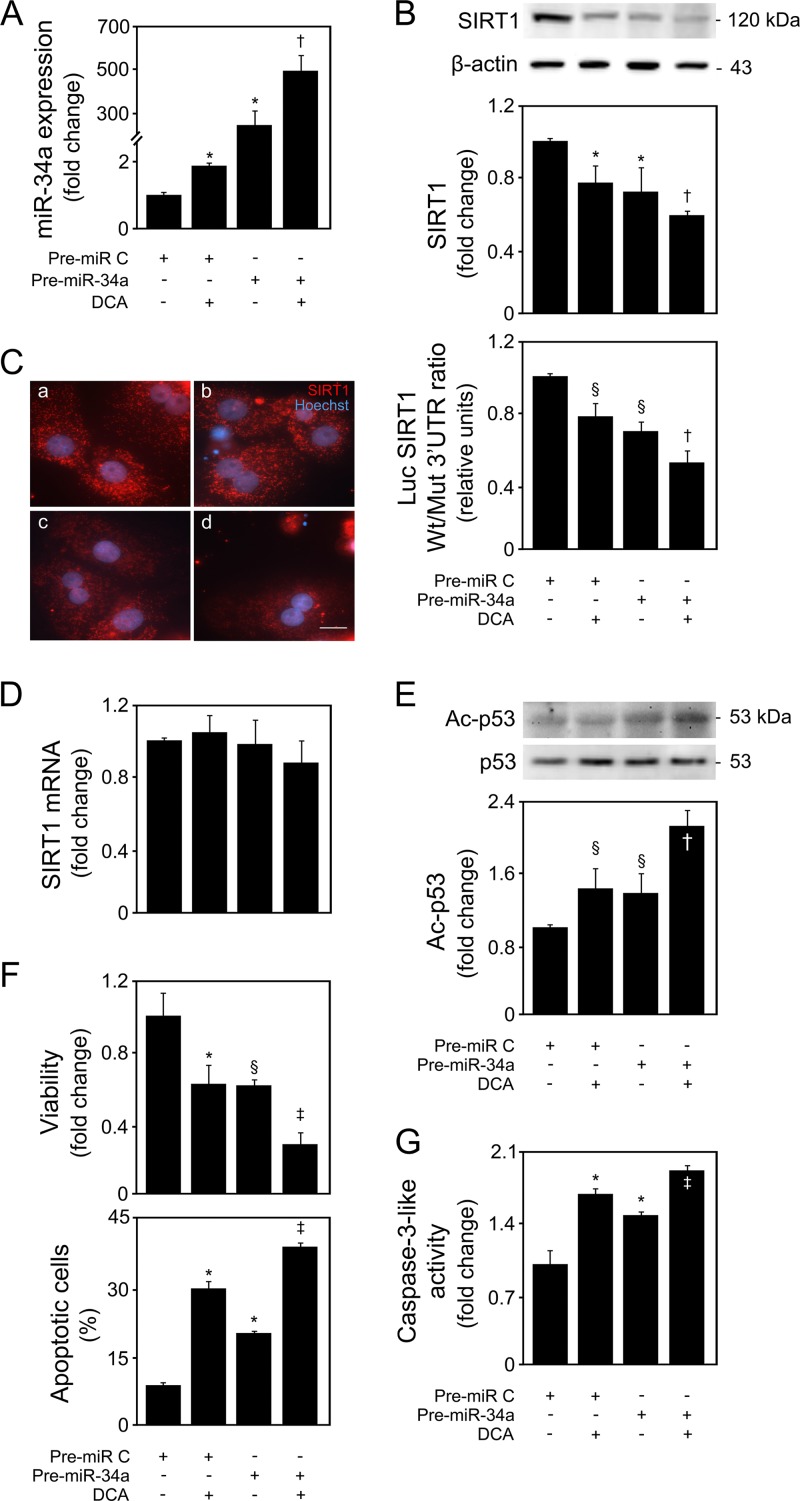
FIG 6.
DCA exacerbates miR-34a-dependent signaling and apoptosis in primary rat hepatocytes. Cells were transfected with an miR-34a precursor (pre-miR-34a) or control (pre-miR control) and treated with 100 μM DCA or no addition (control) for 40 h as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of miR-34a overexpression. (B) Immunoblotting of SIRT1 in cells transfected with the miR-34a precursor (top) and ratio between Wt and Mut SIRT1 3′ UTR luciferase activity (bottom). Representative immunoblots are shown. Blots were normalized to endogenous β-actin. Primary rat hepatocytes were cotransfected with a reporter vector consisting of a luciferase cDNA fused to the 3′ UTR of SIRT1, containing either a wild-type (Wt) or mutant (Mut) miR-34a binding site. The cytomegalovirus-renilla luciferase vector served as an internal standard control. (C) SIRT1 localization determined by immunocytochemistry. SIRT1 staining (red) and Hoechst staining (blue) are shown as control (a), DCA (b), miR-34a overexpression (c), and miR-34a overexpression with DCA treatment (d). Bar, 10 μm. Magnification, ×630. (D) SIRT1 mRNA levels were measured by real-time RT-PCR. (E) Immunoblotting of acetyl-p53 (Ac-p53). Representative immunoblots are shown. Blots were normalized to total p53. (F) Cell viability (top), determined by the ApoTox-Glo triplex assay, and apoptosis (bottom), determined by Hoechst staining. (G) Caspase-3-like activity determined by the ApoTox-Glo triplex assay. Results are expressed as mean (±standard error of the mean) percentage from 6 different experiments. §, P < 0.05, and *, P < 0.01, from pre-miR control; †, P < 0.05, and ‡, P < 0.01, from pre-miR-34a.