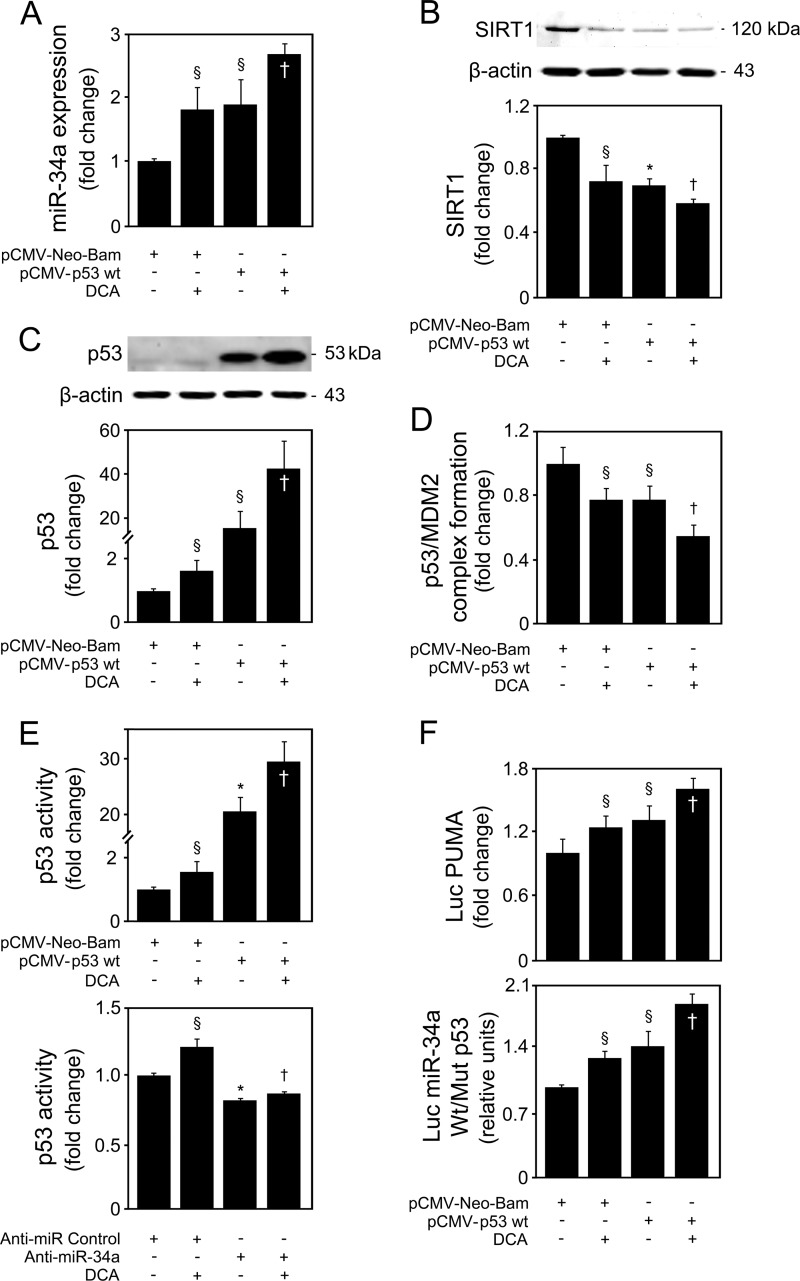
FIG 8.
DCA induces p53-dependent activation of the miR-34a apoptotic pathway in primary rat hepatocytes. Cells were transfected using a pCMV-Neo-Bam vector harboring the wild-type p53 human sequence (pCMV-p53 Wt) or an empty vector (pCMV-Neo-Bam) and treated with 100 μM DCA or no addition (control) for 24 h as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of miR-34a expression. (B) Immunoblotting of SIRT1. (C) Immunoblotting of p53. Representative immunoblots are shown. Protein blots were normalized to endogenous β-actin. (D) p53/MDM2 binding as determined by the ImmunoSet p53/MDM2 complex-specific immunometric enzyme immunoassay and expressed as fold change relative to the control. (E) Levels of nuclear p53 able to bind to its DNA consensus recognition sequence, as determined by the TransAM p53 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with p53 overexpression (top) and miR-34a inhibition (bottom). (F) p53-dependent PUMA and miR-34a promoter activation. Primary rat hepatocytes were cotransfected with a luciferase construct with the PUMA promoter containing consensus p53 binding sites upstream of the transcription start site (Luc PUMA) (top). Alternatively, cells were cotransfected with a pGL4 reporter vector consisting of a luciferase cDNA fused to the miR-34a promoter containing either wild-type (Wt) or mutant (Mut) p53 binding sequence (bottom). Cells were also cotransfected with a cytomegalovirus-renilla luciferase vector as an internal standard. Results are expressed as mean (±standard error of the mean) fold change from 5 different experiments. §, P < 0.05, and *, P < 0.01, from pCMV-Neo-Bam alone; †, P < 0.05, from pCMV-Neo-Bam with DCA.