FIG 1.
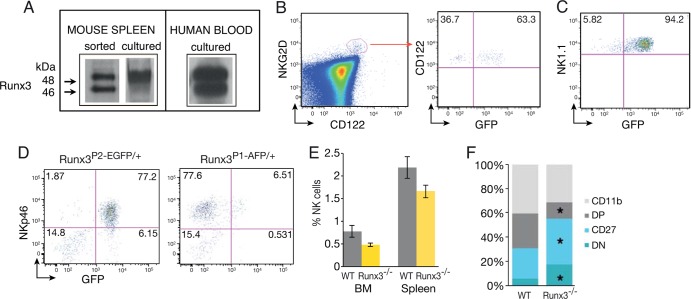
Runx3 is expressed in NKC from the NKP stage, and its loss affects their maturation. (A) Western blot analysis of FACS-sorted mouse spleen NKC (NK1.1+ CD3−), IL-2-cultured mouse spleen NKC, and IL-2-cultured human blood NKC reveals expression of Runx3. (B) NKP cells express Runx3. BM of compound Runx3P1-AFP/+/P2-EGFP/+ mice was analyzed for GFP expression in Lin− (Lin = Ter119, B220, Gr1, CD3, CD8, and CD11b) NK1.1− NKG2D+ CD122+ NKPs. (C) Most NK1.1+ NKC express Runx3. Lin− NK1.1+ cells of compound Runx3P1-AFP/+/P2-EGFP/+ mice were analyzed for GFP expression. (D) Analysis of Runx3P1-AFP/+ and Runx3P2-EGFP/+ expression in BM. CD122+ CD3− BM lymphocytes were analyzed for coexpression of NKp46 and either P1- or P2-derived GFP expression. (E) Percentages of NKp46+ NKC in BM and spleen of WT and Runx3−/− mice. (F) Bar graphs showing the frequency of WT and Runx3−/− NKC subsets out of total NKp46+ spleen cells under resting conditions. Mean values are shown for the four maturation stages of NKC (n = 5). Significance, WT versus Runx3−/− NKC: ∗, P < 0.05. CD11b, CD11b+ CD27−; DP, CD11b+ CD27+; CD27, CD11b− CD27+; DN, CD11b− CD27−.