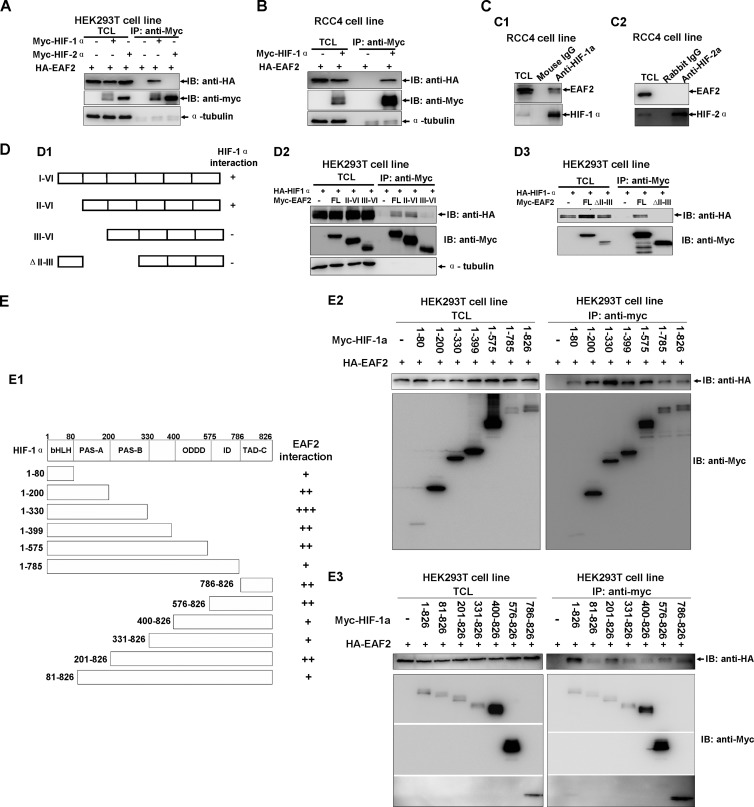
FIG 2.
EAF2 interacts with HIF-1α in vitro and in vivo. (A) EAF2 interacts with HIF-1α but not HIF-2α, as revealed by coimmunoprecipitation assays. Myc-HIF-1α, Myc-HIF-2α, and HA-EAF2 were transiently transfected into HEK293T cells, and anti-Myc antibody-conjugated agarose beads were used for immunoprecipitation. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation between transfected Myc-HIF-1α and HA-EAF2 in RCC4 cells. (C) Endogenous EAF2 interacted with endogenous HIF-1α in RCC4 cells, but EAF2 did not interact with HIF-2α in RCC4 cells. (D1) Schematic of EAF2 domains. (D2 and D3) Coimmunoprecipitation between transfected Myc-EAF2 domains and HA-HIF-1α in HEK293T cells. (E1) Schematic of HIF-1α domains. The extent of the interaction between EAF2 and HIF-1α domain is indicated by the number of plus signs. (E2 and E3) Coimmunoprecipitation between transfected Myc-HIF-1α domains and HA-EAF2 in 293T cells. TCL, total cell lysate; IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot.