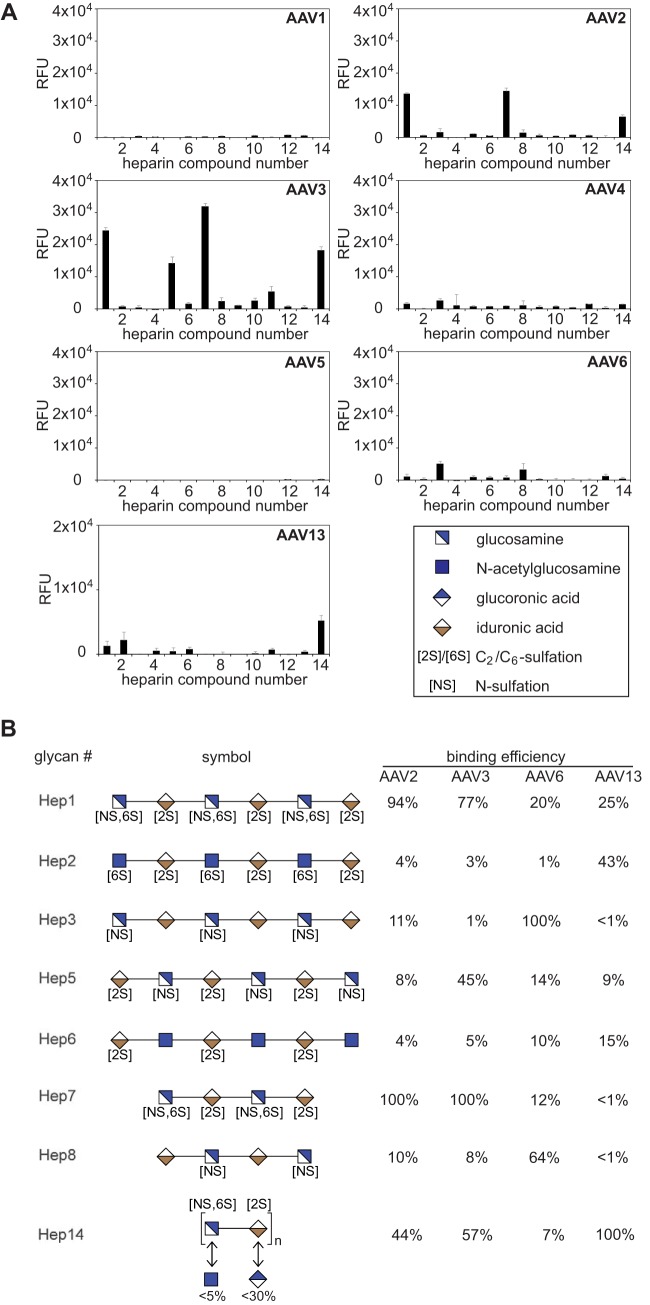
FIG 4.
Heparin array screening of AAV serotypes 1 to 6 and 13. (A) Binding efficiencies of fluorescently labeled AAV1 to -6 and -13 vectors on heparin arrays displaying 13 different synthetic heparin structures and low-molecular-weight natural heparin 14, each in replicates of 10. Note that the binding signals of AAV13 were obtained from arrays displaying lower concentrations (0.25 mM) of the various heparin variants in contrast to all other AAV serotypes (1 mM). The error bars represent standard deviations. (B) Heparins that were identified in panel A to interact with the capsids of a particular serotype (42). Shown is a comparison of AAV serotype-dependent binding to related glycan structures present on the heparin array. Relative binding efficiencies are represented as percentages of that of the most efficiently binding glycan for the depicted AAV serotype.