FIG 7.
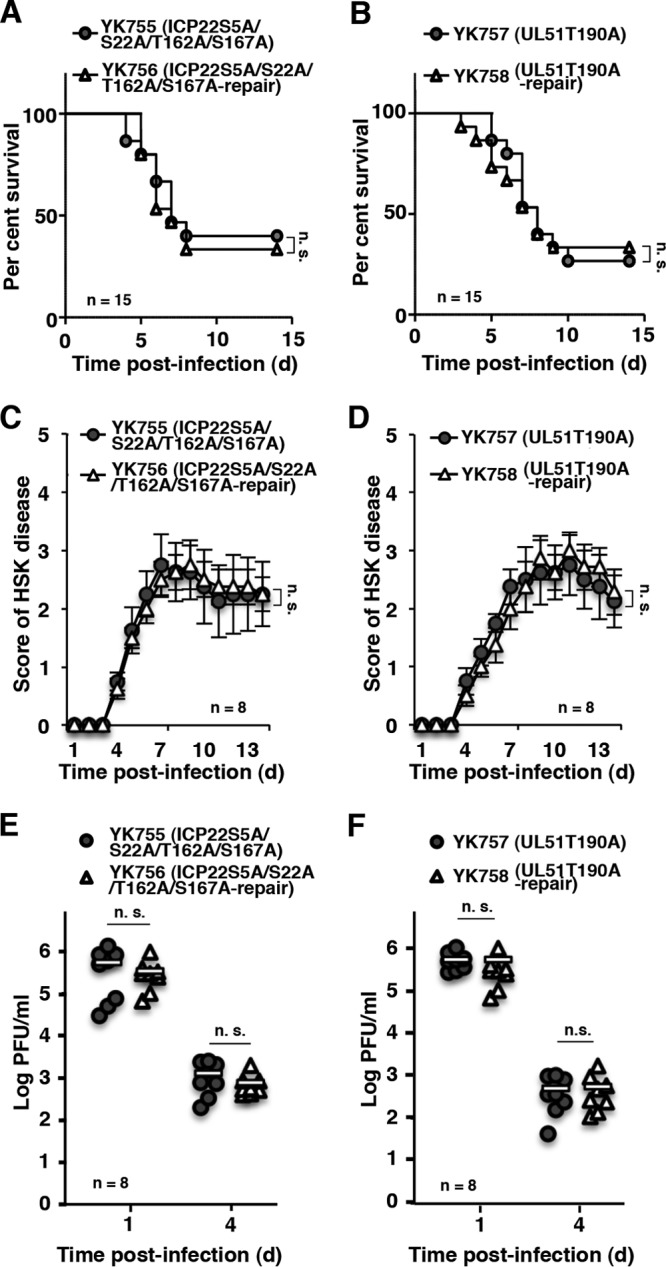
Effect of phosphorylation of other viral proteins on viral pathogenicity and replication in mice. (A and B) Fifteen 3-week-old female ICR mice were infected intracranially with YK755 (ICP22S5A/S22A/T162A/S167A) and YK756 (ICP22S5A/S22A/T162A/S167A-repair) (A) or YK757 (UL51T190A) and YK758 (UL51T190A-repair) (B), and the survival of infected mice was monitored for 14 days postinfection. (C and D) Eight 5-week-old female ICR mice were ocularly infected and scored for severity of HSK every day for 14 days postinfection with YK755 (ICP22S5A/S22A/T162A/S167A) and YK756 (ICP22S5A/S22A/T162A/S167A-repair) (C) or with YK757 (UL51T190A) and YK758 (UL51T190A-repair) (D). Each data point is the mean ± the standard error of the observations. (E and F) The tear films of infected mice at 1 and 4 days postinfection in the experiments described in panels C and D, respectively, were harvested, and virus titers were assayed. Each data point is the virus titer in the tear film of one mouse. The horizontal bars indicate the mean for each group. The statistical significance values were analyzed according to the log-rank test (A and B) or the two-tailed Student t test (C to F). n.s., not significant.
