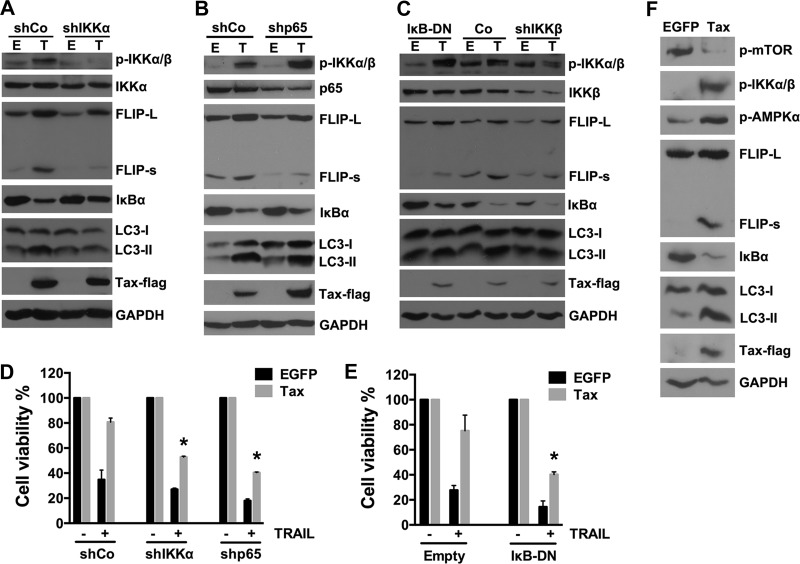
FIG 6.
Activation of NF-κB is necessary for Tax-induced c-FLIP expression but not for Tax-increased autophagosome accumulation. (A to C) U251 cells were infected with LVs encoding no shRNA sequence (shCo), an shRNA targeting IKKα (A), IKKβ (C), or p65 (B), or IκB-DN mutant genes (C) for 3 days and then infected with LV-EGFP or LV-Tax. The knockdown efficacy, IκBα degradation, and c-FLIP and LC3-II expression levels were analyzed by Western blotting. (D and E) IKKα (D), p65 (D), and IκBα (E) contribute to Tax-induced TRAIL resistance. After the infection of the cells with LVs as described for panels A to C, the U251 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of 50 ng/ml TRAIL for 12 h. Cell viability was then determined via MTS assays (mean ± SD; n = 3; *, P < 0.01 compared with TRAIL-treated cells expressing Tax and shCo [D] or Tax and Empty [E]). (F) AMPKα and mTOR are involved in Tax-increased autophagosome accumulation. U251 cells were infected with LVs; 4 days after infection, the cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting to determine IKK and AMPKα activation, mTOR inhibition, and c-FLIP and LC3-II expression levels.