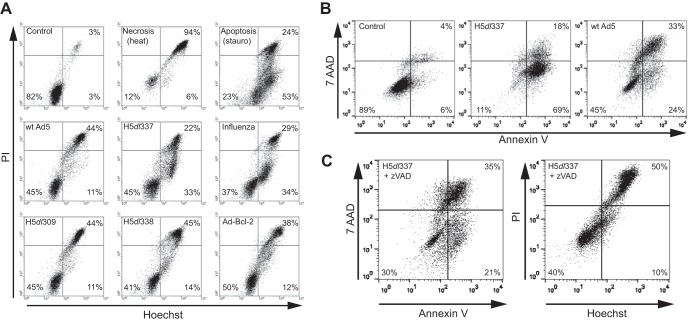
FIG 1.
Nonapoptotic cell death induced by Ad5 infection is dependent on the expression of the adenoviral E1B 19K protein. (A) Changes in Hoechst/PI staining of A549 cells following either 48-h infection with different Ads or 24-h infection with influenza A virus. Viable (Control), necrotic (heat), and apoptotic (stauro) A549 cells were used as controls. Infection of A549 cells with wt Ad5, H5dl309, H5dl338, or Ad-Bcl-2 resulted in nonapoptotic cell death as evidenced by Hoechst/PI staining that was primarily Hoechst+/PI+, a pattern similar to that seen with necrotic (heat) A549 cells. In contrast, H5dl337 and influenza A virus infection resulted in apoptotic cell death, as evidenced by accumulation of Hoechst+/PI− cells (lower right quadrant of the cytograms), prior to loss of cell membrane integrity when cells were permeable to PI (Hoechst+/PI+ staining), a pattern similar to that observed with apoptotic (stauro) cells. (B) Externalization of phosphatidylserine residues as an indicator of apoptotic cell death. Forty-eight hours postinfection, cells were harvested and stained with annexin V and 7-AAD to assess cell surface phosphatidylserine exposure and cell membrane integrity, respectively. Infection of A549 cells with H5dl337 resulted in apoptotic cell death, as evidenced by the high percentage of cells showing phosphatidylserine residue externalization, prior to loss of cell membrane integrity (annexin V+/7-AAD− cells). In contrast, infection of A549 cells with E1B 19K-competent wt Ad5 resulted in repression of phosphatidylserine residue externalization prior to loss of membrane integrity, compared with cells infected with E1B 19K-negative H5dl337 (i.e., 24% versus 69% annexin V+/7-AAD− cells in right lower quadrants, respectively). (C) Caspase dependence of H5dl337-induced apoptotic cell death. A549 cells were infected with H5dl337 in the presence of zVAD (50 μM). Forty-eight hours postinfection, cells were harvested and stained with either annexin V/7-AAD or Hoechst/PI, to examine the caspase dependence of phosphatidylserine residue externalization or DNA condensation prior to loss of cell membrane integrity, respectively. Infection with H5dl337 in the presence of zVAD blocked the apoptotic phenotype and resulted in a reduction in the annexin V+/7-AAD− and Hoechst+/PI phenotypes of infected cells, resulting in a staining pattern that was identical to that seen with wt Ad5 infection (compare panel C results with those for wt Ad5 in panels A and B).