FIG 3.
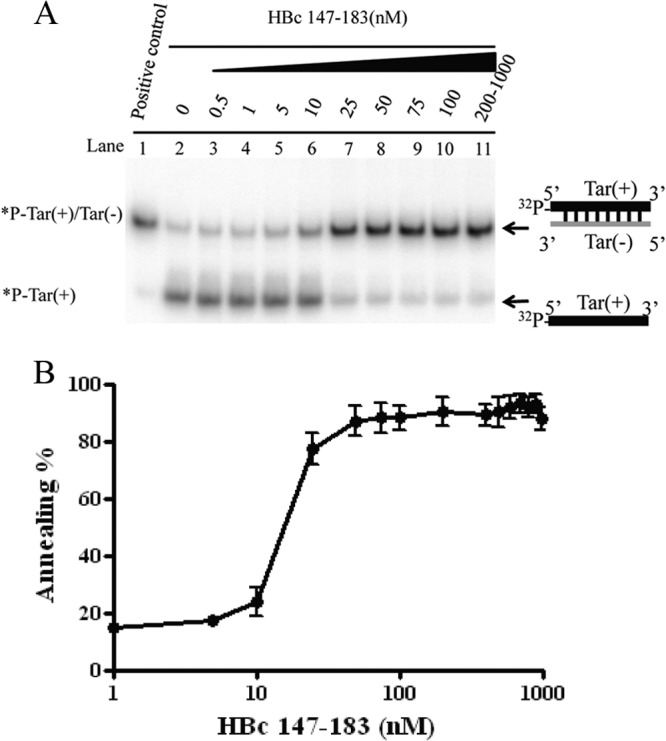
The arginine-rich domain (ARD) of HBc 147-183 exhibits DNA annealing activity. (A) DNA annealing activity is dependent on HBc ARD peptides in a dose-dependent manner. Annealing of Tar(+)/Tar(−) was promoted by HBc ARD peptides. 32P-labeled Tar(+) DNA (1 nM) was incubated with unlabeled Tar(−) DNA (1 nM) in the presence of increasing amounts of HBV core peptides HBc 147-183 (0.5 to 1000 nM) at 37°C for 5 min. (B) The annealing reaction is plotted against HBc ARD peptide concentrations based on the data in panel A. The reaction kinetics appeared to be cooperative after 10 nM before reaching a plateau. The annealing activity (percent) was calculated as the ratio of the banding intensities between duplex molecules and total intensities: [32P-labeled Tar(+)/Tar(−)]/{[32P-labeled Tar(+)/Tar(−)] + 32P-labeled Tar(+)}.
