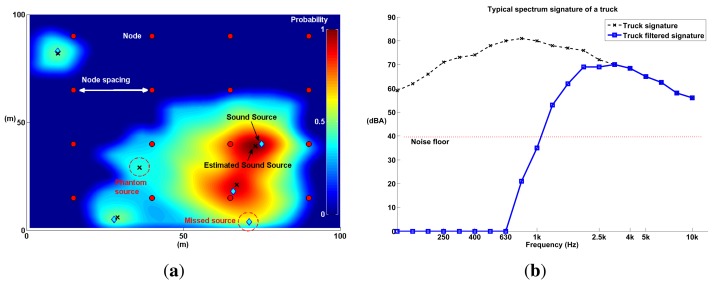
Figure 14.
Several simulations of a wireless sensor network (WSN) equipped with a SoundCompass on each node on a 100 m × 100 m open field were performed. The spectrum signature of a heavy truck was used as a test sound source in most simulations. Several variables were iterated (node spacing, number of sound sources, angle resolution, sound source frequency, etc.) to measure the performance of the localization technique. (a) A node grid spaced 25 m apart accurately detects four out of five sound sources. The map shows two kinds of map errors: a miss (a not detected sound source or false negative) and a phantom (a false positive). (b) The typical frequency spectrum of a heavy truck [23] has a peak at around 1 kHz. However, to improve the localization accuracy, frequencies below 1,630 Hz must be filtered out. The blue line is the result of filtering the truck signature with a high pass filter, and the red line represents the simulated noise floor in all microphone arrays.