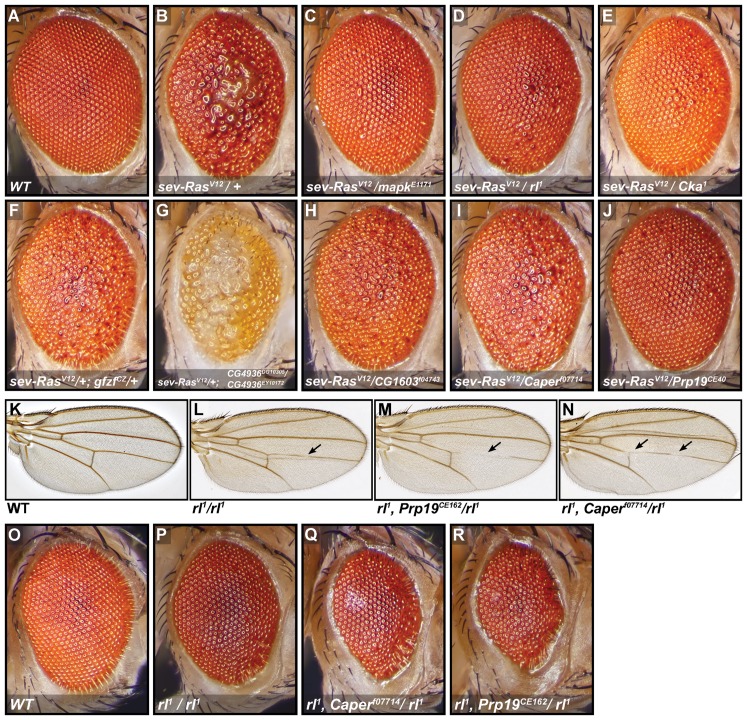
Figure 6. RNAi screen candidates interact genetically with RAS/MAPK pathway components.
(A–J) The RasV12 rough eye phenotype is dominantly suppressed by heterozygous mutations in Cka, gfzf, CG1603, Fip1, Prp19, Caper, and a trans-heterozygous mutation in CG4936. Fly eyes of the indicated genotypes were imaged by stereomicroscopy. The mapk alleles mapkE1171 and rl1 are used as positive controls. All fly eye images are from female flies except CG4936DG10305/CG4936EY10172, which is from a male fly; the rough eye phenotype was observed to be similar in males and females except in this case where males displayed a stronger genetic interaction. (K–N) Genetic interactions with rl1 wing vein deletion phenotypes. rl1/rl1 flies display a slight deletion of the mid-section of the L4 wing vein that is not fully penetrant. The L4 deletion is enhanced, sometimes extending to the posterior cross vein (pcv) in Prp19CE162 and Caperf07714 heterozygous backgrounds (pictures shown served to illustrate detailed scoring results in Figure S8H). (O–R) Genetic interactions with rl1 rough-eye phenotypes. The weak rough eye phenotype observed in rl1 homozygotes is shown. The severity of this phenotype is increased in heterozygous mutant backgrounds for Prp19 and Caper; these flies display a further decrease in eye size and an increased eye roughness.