Figure 1.
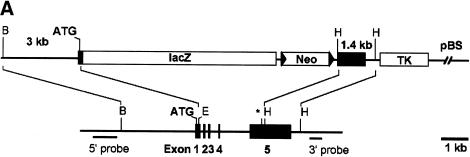
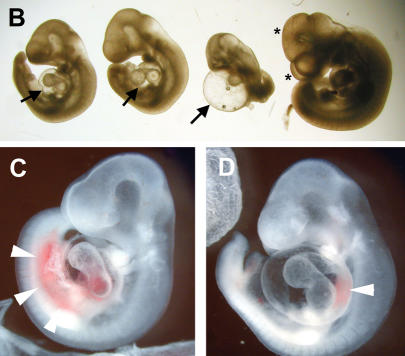
Knockout of the Hey1 locus and embryonic death of Hey1/2 DKO embryos. (A) The targeting construct is depicted above the mouse genomic Hey1 locus containing five exons. Homology regions of 3 kbp (BglII/Ecl136II) and 1.4 kbp (HindIII) containing mainly promoter and 3′untranslated regions, respectively, were used for recombination. The PGK-neo cassette (Neo) is flanked by loxP sites (triangles) for subsequent removal by cre-recombinase. The HSV-TK (TK) cassette was included for negative selection. Flanking genomic probes used for Southern blot hybridization are highlighted by thick lines. (B) BglII; (E) Ecl136II; (H) HindIII; (*) stop codon; (pBS) pBluescript cloning vector backbone. (B) At E10.5, the Hey1/2 DKO embryos can be clearly identified. They are much smaller compared to a het/het littermate (fourth embryo), and they lack prominent mes- and telencephalic vesicles (*). The extensive pericardial sac is highlighted by arrows. (C,D) Already at E9.5, most DKO embryos suffer from massive hemorrhage in the trunk (arrowheads, C) or the pericardial sac (D).