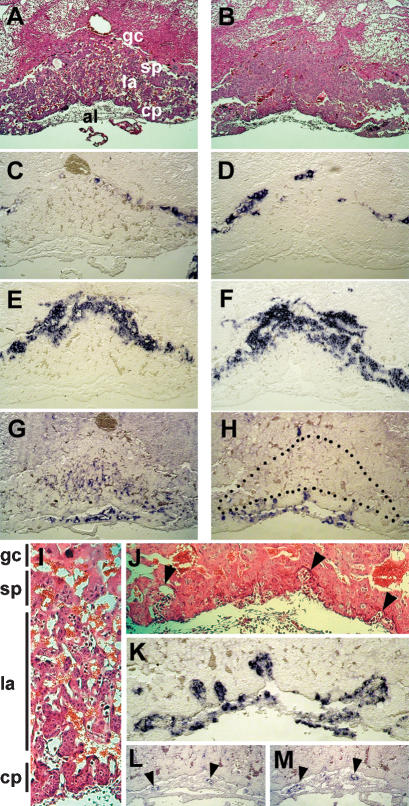
Figure 2.
Placental defects in Hey1/2 DKO mice. A layered structure is visible at E10.5 in both normal (A,C,E,G,I) and Hey1/2 DKO (B,D,F,H) placentas. (A,B) H&E staining shows a close intermingling between maternal blood spaces with small erythrocytes and embryonic vessels with larger, nucleated red blood cells in the control placenta. Especially the labyrinth in the DKO placenta appears cell-rich and devoid of embryonic vessels. (C,D) The giant cell border between the maternal and the embryonic compartment stains positive with a Csh1 (placental lactogen 1) probe. (E,F) Tpbpa (4311) marks the spongiotrophoblast layer that appears unaltered in DKO placentas. (G,H) Vegfr2 (Flk1) stains endothelia of all embryonic vessels in the labyrinth and the chorioallantoic plate. A dotted line highlights the labyrinthine region in DKO mutants, which lacks any staining. (J,K) Fetal vessels only start to invade the trophoblast layer, but fail to branch and extend any further as seen by H&E (J) and endothelial Vegfr2 (K) staining. Abortive buds are marked by triangles. (I) In a control placenta, the labyrinthine layer is characterized by intermingling and close apposition of maternal and embryonic blood spaces to facilitate nutrient and gas exchange. (L,M) Both Hey1 and Hey2 are expressed in endothelia of embryonic vessels in the chorioallantoic plate (arrowheads) of controls and faintly if at all in the embryonic labyrinth. (gc) Giant cells; (sp) spongiotrophoblast; (la) labyrinth; (cp) chorionic plate; (al) allantois.