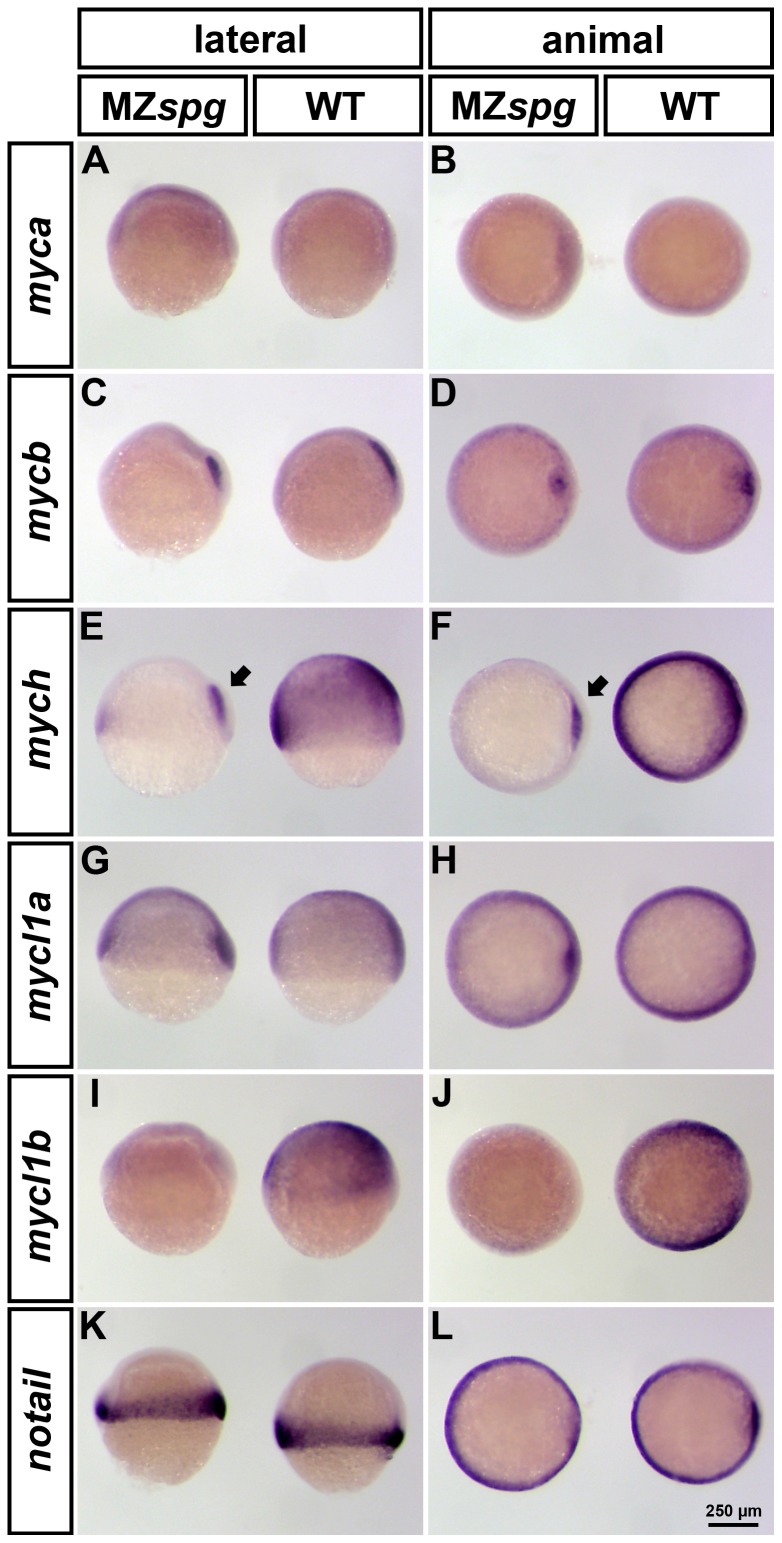
Figure 1. Spatial expression pattern of zebrafish myc genes in WT and MZspg embryos at 60% epiboly.
Whole mount in situ hybridization (WISH) analysis of myca, mycb, mych, mycl1a and mycl1b expression in WT (right embryo in each panel) and MZspg (left embryo in each panel). All embryos are shown in lateral (left column) and animal (right column) views with dorsal oriented to the right. All analyzed myc genes are broadly expressed in mid-gastrula embryos, except for c-myc homologues, myca and mycb. mycb is specifically expressed in the shield, whereas myca was not detectable at this stage (A-D). mych and mycl1a in addition have a strong expression domain in the involuting axial mesoderm (E-H). Only mych (E-F) and mycl1b (I-J) depend on the function of Pou5f1 and their expression is strongly decreased in MZspg mutants. However, the mych expression domain in the involuting axial mesoderm is less affected in Pou5f1 deficient embryos (E-F; arrows). We used notail as control, because its expression is not altered in MZspg mutants compared to WT (K-L).