Figure 1.
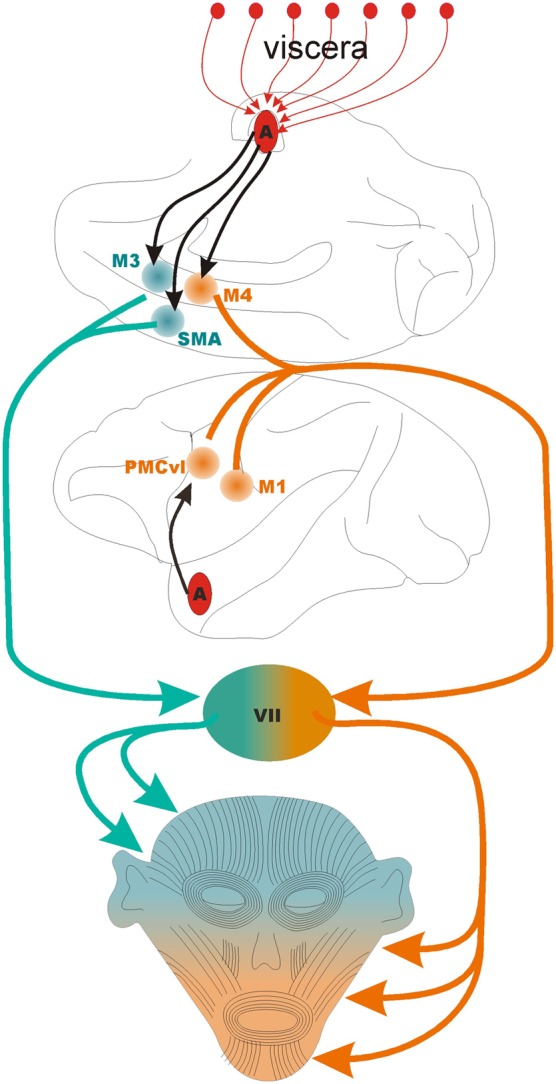
The motor control of the face. The lower half of the face is controlled by the coordinated activity of three motor areas: M1, primary motor cortex; PMCvl, premotor cortex ventrolateral division; and M4, caudal face area of the midcingulate cortex. The upper half of the face is controlled by the coordinated activity of two motor areas: SMA, supplementary motor area; and M3, the anterior face area of the midcingulate cortex. The black arrows indicate direct projections from the basal nucleus of the amygdala to PMCvl, M3, M4, and SMA, The first segment of the orange and green lines indicate the corticobulbar tract. VII, pontine facial nucleus that contain the motor neurons that synapse on the muscles of facial expressions. The medial division of the facial nucleus contains the motor neurons that control muscles in that upper half of the face (in green) while the lateral division contains the neurons that control the muscles in the lower part of the face (in orange). Note that the amygdala receives multiple lines of viscerosensory input (red arrows, top) that are likely integrated in the output directed at facial motor areas.
