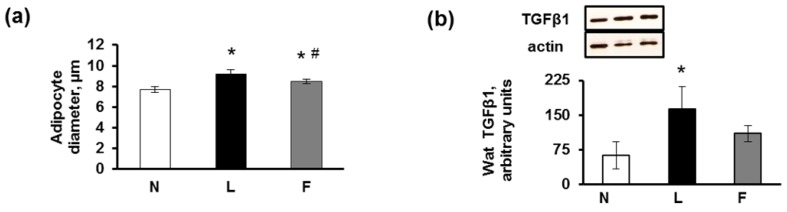
Figure 2.
(a) Adipocyte diameter: The mean diameter of the L adipocytes was significantly higher compared with that of the F group. The mean adipocyte diameters of both the L and the F rats were significantly higher than that of the N group. The data represent the means ± SE (100 cells/animal, 8 animals/group). * p < 0.05 vs. N rats; and # p < 0.05 vs. L rats; (b) Representative Western blot analysis of TGFβ1 and corresponding densitometric analysis on the relative protein levels. The data represent the means ± SE. * p < 0.05 vs. N rats; (c) Histological sections of rats fed a control diet (N), high-lard diet (L) or high-fish oil diet (F) that indicate the presence and relative abundance of crown-like structures (CLSs) around hypertrophic adipocytes. No CLSs were observed in the N rats; (d) Immunostaining of histological sections of the N, L and F rats. MCP1: No immunostaining for MCP1 was observed in the N rats. Immunoreactivity was present in CLSs (dashed arrow) and in the rim of the cytoplasm of adipocytes in the L and F rats (arrow). TGFβ1: The immunostaining was weak in the N section, whereas the L section demonstrated the strongest immunostaining among the groups. InsR (insulin receptor): Following insulin administration (15 min after an i.p. injection of insulin (homologue rapid-acting, 10 units/kg body wt; Novartis)), the N and F eWAT sections exhibited strong immunoreactivity in some areas (arrows), whereas weak immunoreactivity was localised in the L adipocytes (arrows). Glut4: After the insulin injection, the immunostaining for the glucose transporter Glut4 demonstrated an identical distribution as that of InsR and was evident in N and F (arrows) sections, whereas the L section demonstrated weak Glut4 immunostaining that occurred in areas with apparent stromal-vascular cell localization (arrows). PPARγ: Immunoreactivity was observed in the adipocyte cytoplasm and in the vascular stromal cells in all groups of rats. In the F rats, we found the highest immunolabelling of both adipocyte cytoplasm and nuclei, which was consistent with the translocation of PPAR into the nuclei (arrows).