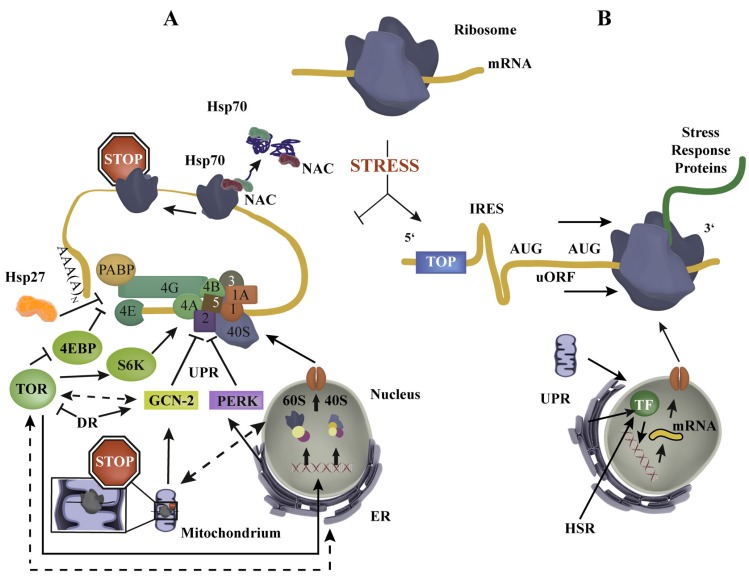
Fig. (1).
Protein synthesis regulation in stress – an overview. (A) Upon stress (e.g. dietary restriction, heat shock) global protein synthesis is reduced by a complex cross-compartmental network of stress response pathways (TOR, GCN-2, PERK), which interact with components of the eIF4F complex (eIF4A, eIF4E, eIF4G) and 43S (40S, eIF1, eIF1A, eIF2, eIF3, eIF5) and thereby disturb mRNA translation initiation [15]. Dotted lines indicate general pathway interconnections which can be activating and/or inhibiting. Chaperones also regulate mRNA translation either by ribosome dissociation, which causes ribosomal stalling (NAC, Hsp70) or by interaction with PABP/eIF4G (Hsp27). (B) Enhanced synthesis of stress response proteins, e.g. chaperones, degradation machineries, transcriptions factors (TF), is mediated by IRES, uORFs and TOP elements, enabling protein synthesis in conditions where global mRNA translation is reduced. Cytosolic, mitochondrial and ER stress responses recruit TFs (e.g. HSF-1, ATFS-1, XBP-1) to induce compartment-specific stress response protein production.