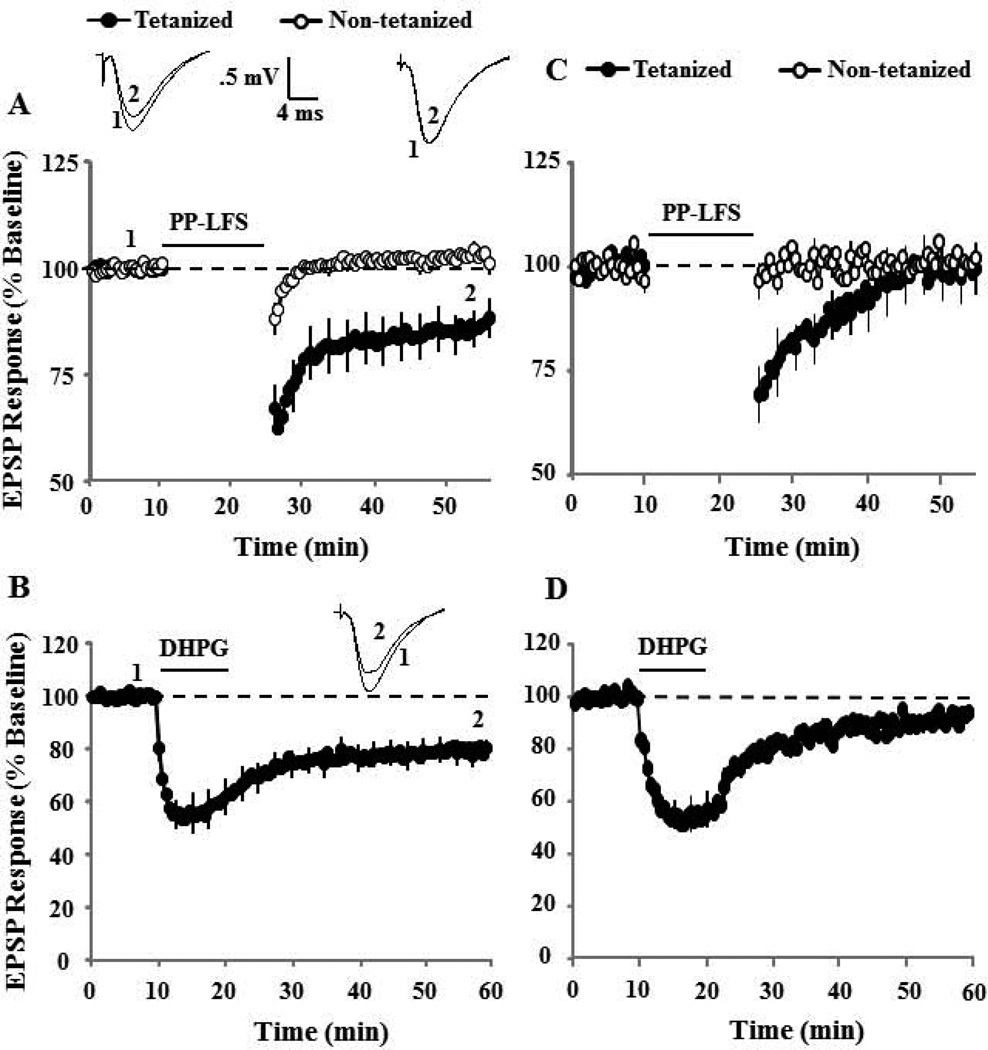
Figure 5.
The combination of NMDAR and L-type voltage gated Ca2+ channel antagonism blocks synaptic-LTD and DHPG-LTD. A) Time course of changes in the EPSP responses for the tetanized (filled symbol) and control (open symbols) pathways in the presence of nifedipine (10 µM, n = 9). The inserts are representative traces of the EPSP responses from tetanized (left) and control (right) pathway for the indicated time points. B) Time course of synaptic responses showing the effect of DHPG application (solid line), in the presence of nifedipine (n = 9). The inserts are representative traces of the EPSP responses before (1) and after (2) DHPG application. Blockade of NMDAR and L-type Ca2+ channels significantly attenuated synaptic and DHPG-LTD. C) Time course of changes in the EPSP responses for the tetanized (filled symbol) and control (open symbols) pathways in the presence of AP-5 + nifedipine (n = 6). D) Time course of synaptic responses showing the effect of DHPG application (solid line) in the presence of AP-5 + nifedipine (n = 8).