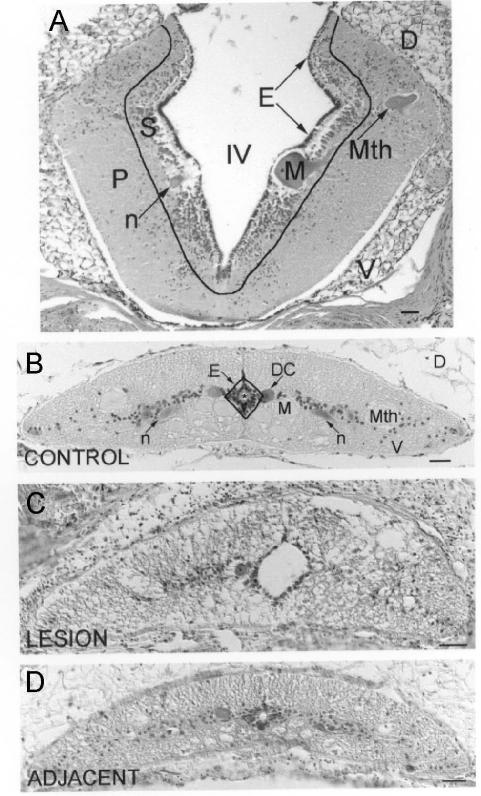
Fig. 1. Cytoarchitecture of the lamprey rhombencephalon and spinal cord.
Hematoxylin-stained CNS cross-sections are shown with outlines indicating boundaries between adjacent cytoarchitectonic regions. A, the rhombencephalon is divided into ependyma (E), subventricular zone (S), and peripheral region (P). IV = fourth ventricle ; D = Dorsal; V = ventral; Mth = Mauthner neuron ; M = Müller neuron ; n = neuron. B, the spinal cord is divided into ependyma (E), a diamond shaped, pseudostratified layer of cells 2 – 3 nuclei deep that surround the central canal, and the non-ependyma. Mth = Mauthner axon; M = Müller axon; n = neuron; DC = dorsal cell. C, lesioned spinal cord. Note the enlarged central canal, the asymmetrical shape of the spinal cord in comparison with the control, and the absence of landmarks such as the Mauthner axons in the lateral spinal cord. D, spinal cord adjacent to the lesion. * = central canal; D = dorsal; V = ventral; scale = 50 μm.