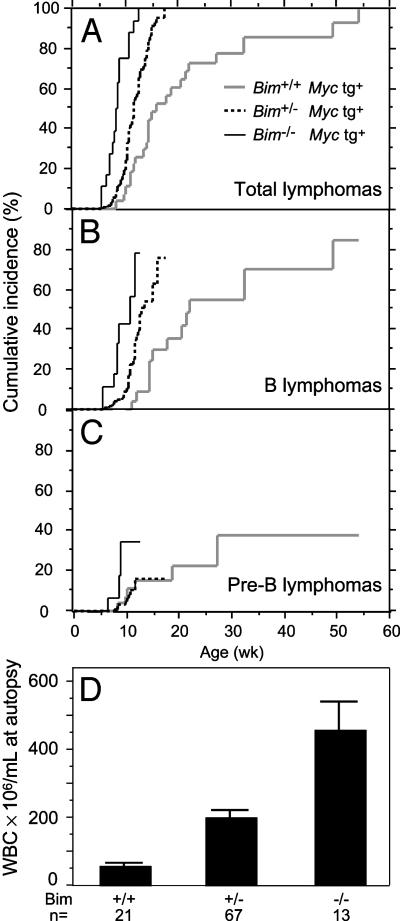
Fig. 1.
Loss of Bim accelerates lymphoma development initiated by Eμ-Myc transgene. (A) Cumulative incidence of all tumors in mice of the indicated genotype. Tumors occurred earlier in Bim+/- mice (P < 0.0001) and Bim-/- mice (P < 0.0001) than in Bim+/+ mice. (B) B cell lymphoma development was accelerated in Eμ-Myc mice by the loss of one allele (P = 0.0008) or two alleles of Bim (P < 0.0001). (C) Pre-B lymphoma development was not altered in Bim+/- mice (P = 1), and a trend toward earlier onset in Bim-/- mice was not statistically significant (P = 0.1). (D) Frequency of total leukocytes in the blood of sick Eμ-Myc mice of indicated Bim genotype. Bim+/- mice had higher leukocyte counts than Bim+/+ mice (P < 0.0001), and Bim-/- mice had significantly higher counts than in either Bim+/- (P < 0.0001) or in Bim+/+ mice (P < 0.0001). The Bim-/- and Bim+/- mice had much higher numbers of B cells than did Bim+/+ mice (P < 0.0001 and P = 0.003, respectively). Pre-B cell numbers were somewhat higher in the Bim-/- mice than in the Bim+/+ mice (P = 0.01), but were comparable in the Bim+/- mice (P = 0.9). Leukocyte counts were 7.9 ± 0.3 × 106 per ml in 45 healthy wild-type C57BL/6 mice and 16 ± 3 × 106 per ml in 39 healthy 3-wk-old Eμ-Myc Bim+/+ mice.